Identification of Hub Genes With Differential Correlations in Sepsis
- PMID: 35401666
- PMCID: PMC8987114
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.876514
Identification of Hub Genes With Differential Correlations in Sepsis
Abstract
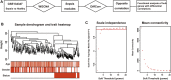
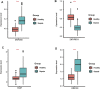
As a multifaceted syndrome, sepsis leads to high risk of death worldwide. It is difficult to be intervened due to insufficient biomarkers and potential targets. The reason is that regulatory mechanisms during sepsis are poorly understood. In this study, expression profiles of sepsis from GSE134347 were integrated to construct gene interaction network through weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA). R package DiffCorr was utilized to evaluate differential correlations and identify significant differences between sepsis and healthy tissues. As a result, twenty-six modules were detected in the network, among which blue and darkred modules exhibited the most significant associations with sepsis. Finally, we identified some novel genes with opposite correlations including ZNF366, ZMYND11, SVIP and UBE2H. Further biological analysis revealed their promising roles in sepsis management. Hence, differential correlations-based algorithm was firstly established for the discovery of appealing regulators in sepsis.
Keywords: WGCNA; biological analysis; differential correlation; regulatory network; sepsis.
Copyright © 2022 Sheng, Tong, Zhang and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Abe T., Yamakawa K., Ogura H., Kushimoto S., Saitoh D., Fujishima S., et al. (2020). Epidemiology of Sepsis and Septic Shock in Intensive Care Units between Sepsis-2 and Sepsis-3 Populations: Sepsis Prognostication in Intensive Care Unit and Emergency Room (SPICE-ICU). j intensive care 8 (1). 10.1186/S40560-020-00465-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

