Clinical Effect of Acupuncture Combined with Traditional Chinese Medicine Application on the Treatment of Functional Dyspepsia in Children and the Influence on Serum 5-HT and NO Levels
- PMID: 35401711
- PMCID: PMC8989592
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6800662
Clinical Effect of Acupuncture Combined with Traditional Chinese Medicine Application on the Treatment of Functional Dyspepsia in Children and the Influence on Serum 5-HT and NO Levels
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Clinical Effect of Acupuncture Combined with Traditional Chinese Medicine Application on the Treatment of Functional Dyspepsia in Children and the Influence on Serum 5-HT and NO Levels.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Dec 18;2022:9875174. doi: 10.1155/2022/9875174. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36575677 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To explore the clinical effect of acupuncture combined with traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) application on the treatment of functional dyspepsia (FD) in children and the influence on serum 5-HT and NO levels.
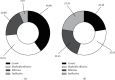
Methods: 94 FD children admitted to the pediatric department of our hospital from March 2019 to March 2020 were selected as the research object and divided into the study group (n = 45) and reference group (n = 49) by the number table method. The routine Western medicine therapy was given to the reference group and the combination therapy of acupuncture and TCM application was given to the study group to analyze the effect of different therapies on FD children by detecting their serum 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and nitric oxide (NO) levels and electrogastrogram (EGG) before and after treatment.
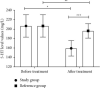
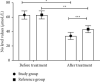
Results: The sex ratio, mean age, mean duration of disease, mean weight, mean BMI value, and residence of children in the two groups were not significantly different (P > 0.05); after treatment, the study group obtained significantly lower symptom scores and shorter disappearance time of clinical symptoms when comparing with the reference group (P < 0.001); the total clinical effective rate of the study group was significantly higher than that of the reference group (P < 0.05); the treated serum 5-HT and NO levels of children in both groups were significantly lower than those before treatment (P < 0.05), and in the between-group comparison, those of the study group were significantly lower (P < 0.05); and the treated AP, FP, and normal slow wave ratio of gastric antrum and body were significantly higher in the study group than in the reference group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The combination therapy of acupuncture and TCM application is a reliable method for improving the clinical symptoms in FD children. This strategy greatly reduces the levels of serum factors in child patients and shortens the corresponding treatment time. Further research will be conducive to establishing a better solution for such patients.
Copyright © 2022 Junxia Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic effects and central mechanism of acupuncture and moxibustion for treating functional dyspepsia: study protocol for an fMRI-based randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2022 Jun 6;23(1):462. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06411-9. Trials. 2022. PMID: 35668441 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical-functional brain connectivity signature predicts longitudinal symptom improvement after acupuncture treatment in patients with functional dyspepsia.Hum Brain Mapp. 2023 Nov;44(16):5416-5428. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26449. Epub 2023 Aug 16. Hum Brain Mapp. 2023. PMID: 37584456 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of manual acupuncture manipulations with different frequencies on epigastric pain syndrome (EPS) in functional dyspepsia (FD) patients: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2017 Mar 6;18(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-1845-3. Trials. 2017. PMID: 28264722 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Electroacupuncture for the treatment of functional dyspepsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Nov 6;99(45):e23014. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023014. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33157947 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of Xin kai bitter method in the treatment of functional dyspepsia.Ann Palliat Med. 2020 May;9(3):993-1003. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-860. Epub 2020 May 8. Ann Palliat Med. 2020. PMID: 32434358
Cited by
-
Retracted: Clinical Effect of Acupuncture Combined with Traditional Chinese Medicine Application on the Treatment of Functional Dyspepsia in Children and the Influence on Serum 5-HT and NO Levels.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Dec 18;2022:9875174. doi: 10.1155/2022/9875174. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36575677 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of treatment of functional dyspepsia with traditional Chinese medicine compound based on cell signal pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 9;13:1089231. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1089231. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36699059 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smeets F. G. M., Keszthelyi D., Vork L., et al. Development of a real‐time patient‐reported outcome measure for symptom assessment in patients with functional dyspepsia using the experience sampling method. Neuro-Gastroenterology and Motility . 2019;31(2) doi: 10.1111/nmo.13496.e13496 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Doi H., Sakakibara R., Masuda M., et al. Gastrointestinal function in dementia with Lewy bodies: a comparison with Parkinson disease. Clinical Autonomic Research: Official journal of the Clinical Autonomic Research Society . 2019;29(6):633–638. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

