Plaque-targeted, proteolysis-resistant, activatable and MRI-visible nano-GLP-1 receptor agonist targets smooth muscle cell differentiation in atherosclerosis
- PMID: 35401813
- PMCID: PMC8965488
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.66456
Plaque-targeted, proteolysis-resistant, activatable and MRI-visible nano-GLP-1 receptor agonist targets smooth muscle cell differentiation in atherosclerosis
Abstract
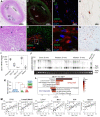
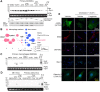
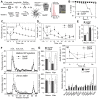
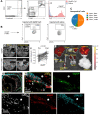
Background: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists are powerful glycemia-lowering agents, which have systematically been shown to lower cardiovascular events and mortality. These beneficial effects were difficult to pinpoint within atherosclerotic plaque due to lack of particular specificity of such agonists to the vascular cells and an inadequate understanding of the GLP-1R expression in atherosclerosis. Here, we hypothesized that the direct engagement of the GLP-1R in atherosclerosis by targeted agonists will alleviate vascular inflammation and plaque burden, even at a very low dose. Methods: The expression of GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R, Glp1r mRNA) in human lesions with pathologic intimal thickening, Apoe-/- mouse atheroma and cultured immune/non-immune cells was investigated using genetic lineage tracing, Southern blotting and validated antisera against human GLP-1R. Protease-resistant and "activatable" nanoparticles (NPs) carrying GLP-1R agonist liraglutide (GlpNP) were engineered and synthesized. Inclusion of gadolinium chelates into GlpNP allowed for imaging by MRI. Atherosclerotic Apoe-/- mice were treated intravenously with a single dose (30 µg/kg of liraglutide) or chronically (1 µg/kg, 6 weeks, 2x/week) with GlpNP, liraglutide or control NPs, followed by assessment of metabolic parameters, atheroma burden, inflammation and vascular function. Results: Humal plaque specimens expressed high levels of GLP-1R within the locus of de-differentiated smooth muscle cells that also expressed myeloid marker CD68. However, innate immune cells under a variety of conditions expressed very low levels of Glp1r, as seen in lineage tracing and Southern blotting experiments examining full-length open reading frame mRNA transcripts. Importantly, de-differentiated vascular smooth muscle cells demonstrated significant Glp1r expression levels, suggesting that these could represent the cells with predominant Glp1r-positivity in atherosclerosis. GlpNP resisted proteolysis and demonstrated biological activity including in vivo glycemia lowering at 30 µg/kg and in vitro cholesterol efflux. Activatable properties of GlpNP were confirmed in vitro by imaging cytometry and in vivo using whole organ imaging. GlpNP targeted CD11b+/CD11c+ cells in circulation and smooth muscle cells in aortic plaque in Apoe-/- mice when assessed by MRI and fluorescence imaging. At a very low dose of 1 µg/kg, previously known to have little effect on glycemia and weight loss, GlpNP delivered i.v. for six weeks reduced triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in plasma, plaque burden and plaque cholesterol without significant effects on weight, glycemia and plasma cholesterol levels. Conclusions: GlpNP improves atherosclerosis at weight-neutral doses as low as 1 µg/kg with the effects independent from the pancreas or the central nervous system. Our study underlines the importance of direct actions of GLP-1 analogs on atherosclerosis, involving cholesterol efflux and inflammation. Our findings are the first to suggest the therapeutic modulation of vascular targets by GlpNP, especially in the context of smooth muscle cell inflammation.
Keywords: GLP-1; MRI; atherosclerosis; nanomedicine; smooth muscle cells.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Liraglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by enhancing AMP-activated protein kinase and cell cycle regulation, and delays atherosclerosis in ApoE deficient mice.Atherosclerosis. 2017 Jun;261:44-51. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.04.001. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Atherosclerosis. 2017. PMID: 28445811
-
Endothelial GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) Receptor Mediates Cardiovascular Protection by Liraglutide In Mice With Experimental Arterial Hypertension.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Jan;40(1):145-158. doi: 10.1161/atv.0000615456.97862.30. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 31747801 Free PMC article.
-
The GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide inhibits progression of vascular disease via effects on atherogenesis, plaque stability and endothelial function in an ApoE(-/-) mouse model.Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2013 Jul;10(4):353-60. doi: 10.1177/1479164113481817. Epub 2013 May 14. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2013. PMID: 23673376
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor action in the vasculature.Peptides. 2019 Jan;111:26-32. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2018.09.002. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Peptides. 2019. PMID: 30227157 Review.
-
Long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists have direct access to and effects on pro-opiomelanocortin/cocaine- and amphetamine-stimulated transcript neurons in the mouse hypothalamus.J Diabetes Investig. 2016 Apr;7 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):56-63. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12463. Epub 2016 Apr 18. J Diabetes Investig. 2016. PMID: 27186357 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1: New Regulator in Lipid Metabolism.Diabetes Metab J. 2024 May;48(3):354-372. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0277. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Diabetes Metab J. 2024. PMID: 38650100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1: a new potential regulator for mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complication.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 May 19;16(1):248. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04369-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40390070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicine for Diagnosis and Treatment of Atherosclerosis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Dec;10(36):e2304294. doi: 10.1002/advs.202304294. Epub 2023 Oct 28. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37897322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thiazolidinediones play a positive role in the vascular endothelium and inhibit plaque progression in diabetic patients with coronary atherosclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Nov 29;9:1043406. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1043406. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36523368 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular imaging nanoprobes and their applications in atherosclerosis diagnosis.Theranostics. 2024 Aug 12;14(12):4747-4772. doi: 10.7150/thno.96037. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39239513 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Verma S, Bhatt DL, Bain SC. et al. Effect of liraglutide on cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and polyvascular disease: results of the LEADER trial. Circulation. 2018;137:2179–83. - PubMed
-
- Drucker DJ. Mechanisms of action and therapeutic application of glucagon-like peptide-1. Cell Metab. 2018;27:740–56. - PubMed
-
- Pujadas G, Drucker DJ. Vascular biology of glucagon receptor superfamily peptides: mechanistic and clinical relevance. Endocr Rev. 2016;37:554–83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

