Metformin in aging and aging-related diseases: clinical applications and relevant mechanisms
- PMID: 35401820
- PMCID: PMC8965502
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.71360
Metformin in aging and aging-related diseases: clinical applications and relevant mechanisms
Abstract
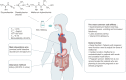
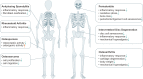
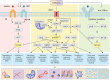
Aging is a natural process, which plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of a variety of diseases, i.e., aging-related diseases, such as diabetes, osteoarthritis, Alzheimer disease, cardiovascular diseases, cancers, obesity and other metabolic abnormalities. Metformin, the most widely used antidiabetic drug, has been reported to delay aging and display protective effect on attenuating progression of various aging-related diseases by impacting key hallmark events of aging, including dysregulated nutrient sensing, loss of proteostasis, mitochondrial dysfunction, altered intercellular communication, telomere attrition, genomic instability, epigenetic alterations, stem cell exhaustion and cellular senescence. In this review, we provide updated information and knowledge on applications of metformin in prevention and treatment of aging and aging-related diseases. We focus our discussions on the roles and underlying mechanisms of metformin in modulating aging and treating aging-related diseases.
Keywords: Metformin; aging; aging-related diseases; clinical application; molecular mechanism..
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Luo J, Mills K, le Cessie S, Noordam R, van Heemst D. Ageing, age-related diseases and oxidative stress: What to do next? Ageing Res Rev. 2020;57:100982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

