Hepatic PRMT1 ameliorates diet-induced hepatic steatosis via induction of PGC1α
- PMID: 35401831
- PMCID: PMC8965489
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.63824
Hepatic PRMT1 ameliorates diet-induced hepatic steatosis via induction of PGC1α
Abstract
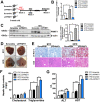
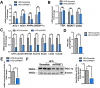
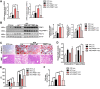
Rationale: Over-nutrition will lead to overexpression of PRMT1 but protein hypomethylation is observed in the liver of obese subjects. The dynamic alteration of the expression and methyltransferase activity of PRMT1 in the progression of fatty liver diseases remains elusive. Methods: We used recombinant adeno-associated virus-mediated gene delivery system to manipulate the hepatic PRMT1 expression level in diet-induced obese mice to investigate the role of PRMT1 in hepatic steatosis. We further utilized a cohort of obese humans with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease to support our observations in mouse model. Results: We demonstrated that knockdown of PRMT1 promoted steatosis development in liver of high-fat diet (HFD) fed mice. Over-expression of wild-type PRMT1, but not methyltransferase-defective mutant PRMT1G80R, could alleviate diet-induced hepatic steatosis. The observation is conserved in the specimens of obese humans with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Mechanistically, methyltransferase activity of PRMT1 was required to induce PGC-1α mRNA expression via recruitment of HNF-4α to the promoter of PGC-1α, and hence attenuated HFD-induced hepatic steatosis by enhancing PGC-1α-mediated fatty acid oxidation. Conclusions: Our results identify that activation of the PRMT1/HNF-4α/PGC-1α signaling is a potential therapeutic strategy for combating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease of obese subjects.
Keywords: Diet-induced hepatic steatosis; HNF-4α; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD); PGC-1α; PRMT1.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Thioredoxin-interacting protein mediates hepatic lipogenesis and inflammation via PRMT1 and PGC-1α regulation in vitro and in vivo.J Hepatol. 2014 Nov;61(5):1151-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.06.032. Epub 2014 Jul 6. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 25003952
-
P2Y2R Deficiency Ameliorates Hepatic Steatosis by Reducing Lipogenesis and Enhancing Fatty Acid β-Oxidation through AMPK and PGC-1α Induction in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 24;22(11):5528. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115528. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34073834 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulatory Impact of CFLAR Methylation Modification on Liver Lipid Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 19;25(14):7897. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147897. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063139 Free PMC article.
-
Neohesperidin enhances PGC-1α-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis and alleviates hepatic steatosis in high fat diet fed mice.Nutr Diabetes. 2020 Aug 5;10(1):27. doi: 10.1038/s41387-020-00130-3. Nutr Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 32759940 Free PMC article.
-
Role of protein arginine methyltransferase 1 in obesity-related metabolic disorders: Research progress and implications.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024 Sep;26(9):3491-3500. doi: 10.1111/dom.15640. Epub 2024 May 15. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024. PMID: 38747214 Review.
Cited by
-
PRMT1 Integrates Immune Microenvironment and Fatty Acid Metabolism Response in Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Jan 6;11:15-27. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S443130. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 38213310 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 1: A Multi-Purpose Player in the Development of Cancer and Metabolic Disease.Biomolecules. 2025 Jan 27;15(2):185. doi: 10.3390/biom15020185. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methylation of BRD4 by PRMT1 regulates BRD4 phosphorylation and promotes ovarian cancer invasion.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Sep 22;14(9):624. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06149-5. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37737256 Free PMC article.
-
The role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in hepatic lipid metabolism.J Mol Med (Berl). 2023 May;101(5):487-500. doi: 10.1007/s00109-023-02308-5. Epub 2023 Mar 28. J Mol Med (Berl). 2023. PMID: 36973503 Review.
-
Protein Arginine Methyltransferases: Emerging Targets in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease.Diabetes Metab J. 2024 Jul;48(4):487-502. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0362. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Diabetes Metab J. 2024. PMID: 39043443 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

