Emerging early diagnostic methods for acute kidney injury
- PMID: 35401836
- PMCID: PMC8965497
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.71064
Emerging early diagnostic methods for acute kidney injury
Abstract
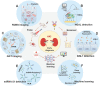
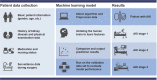
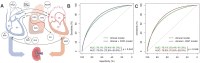
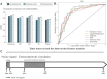
Many factors such as trauma and COVID-19 cause acute kidney injury (AKI). Late AKI have a very high incidence and mortality rate. Early diagnosis of AKI provides a critical therapeutic time window for AKI treatment to prevent progression to chronic renal failure. However, the current clinical detection based on creatinine and urine output isn't effective in diagnosing early AKI. In recent years, the early diagnosis of AKI has made great progress with the advancement of information technology, nanotechnology, and biomedicine. These emerging methods are mainly divided into two aspects: First, predicting AKI through models construct by machine learning; Second, early diagnosis of AKI through detection of newly-discovered early biomarkers. Currently, these methods have shown great potential and become an attractive tool for the early diagnosis of AKI. Therefore, it is very important to discuss and summarize these methods for the early diagnosis of AKI. In this review, we first systematically summarize the application of machine learning in AKI prediction algorithms and specific scenarios. In addition, we introduce the key role of early biomarkers in the progress of AKI, and then comprehensively summarize the application of emerging detection technologies for early AKI. Finally, we discuss current challenges and prospects of machine learning and biomarker detection. The review is expected to provide new insights for early diagnosis of AKI, and provided important inspiration for the design of early diagnosis of other major diseases.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Early diagnosis.; Machine learning; Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; Reactive oxygen species and nitrogen species; kidney injury molecule-1; miRNA-21; γ-glutamyl transpeptidase.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
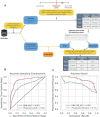

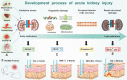


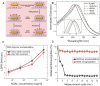
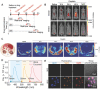

References
-
- Milasinovic D, Mladenovic DJ, Jelic D, Zobenica V, Zaharijev S, Vratonjic J. et al. Relative impact of acute heart failure and acute kidney injury on short- and long-term prognosis of patients with STEMI treated with primary PCI. Eur Heart J. 2021;42:1448. - PubMed
-
- Khruleva YY, Alekseeva M, Troitskaya E, Efremovtseva M, Kobalava Z. Acute decompensated heart failure is a risk factor for acute kidney injury and a predictor of disease severity in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Eur J Heart Fail. 2021;23:193.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

