CD4+FoxP3+CD73+ regulatory T cell promotes cardiac healing post-myocardial infarction
- PMID: 35401839
- PMCID: PMC8965484
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.68437
CD4+FoxP3+CD73+ regulatory T cell promotes cardiac healing post-myocardial infarction
Abstract
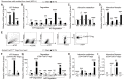
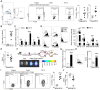
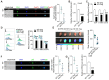
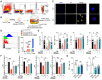
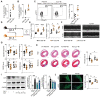
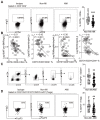
Rationale: Despite recent studies indicating a crucial role of ecto-5'-nucleotidase (CD73) on T cells in cardiac injury after ischemia/reperfusion, the involvement of CD73+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) in cardiac repair post-myocardial infarction (MI) remains unclear. We sought to investigate the contribution of CD73 on Tregs to the resolution of cardiac inflammation and remodeling after MI. Methods: Cardiac function, tissue injury, Tregs percentage in injured hearts, and purinergic signaling changes in cardiac FoxP3+ Tregs were analyzed after permanent descending coronary artery ligation. CD73 knockout Tregs were used to determine the function of CD73 on Tregs. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from acute myocardial infarction (AMI) patients and matched non-MI subjects were assessed via flow cytometry. Results: Cardiac Tregs exhibited distinction of purinergic signaling post MI with dramatically high level of CD73 compared to the sham Tregs. CD73 deficiency decreased the tissue tropism, and impaired the immunosuppressive and protective function of Tregs in cardiac healing. Administration of low-dose of IL-2/anti-IL-2 complex resulted in FoxP3+CD73+Tregs expansion in the heart and contributed to the recovery of cardiac function. CD73 derived from FoxP3+Tregs could bind to FoxP3- effector T-cells and inhibit the production of multiple inflammatory cytokines. In AMI patients, CD73 expressions on both CD4+ cells and FoxP3+Tregs decreased in PBMCs. Moreover, CD73 expressions on CD4+ T cells were negatively correlated with the levels of NT pro-BNP and myocardial zymogram in serum. Conclusions: Our findings indicated the importance of FoxP3+CD73+Tregs in inflammation resolution and cardiac healing post-MI.
Keywords: IL-2/anti-IL-2 complex; Regulatory T cells (Tregs); cardiac healing; ecto-5'-nucleotidase (CD73); myocardial infarction (MI).
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD73 on T Cells Orchestrates Cardiac Wound Healing After Myocardial Infarction by Purinergic Metabolic Reprogramming.Circulation. 2017 Jul 18;136(3):297-313. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.023365. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28432149
-
Adenosine Generated by Regulatory T Cells Induces CD8+ T Cell Exhaustion in Gastric Cancer through A2aR Pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Dec 14;2019:4093214. doi: 10.1155/2019/4093214. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31930120 Free PMC article.
-
CD39/CD73 and the imbalance of Th17 cells and regulatory T cells in allergic asthma.Mol Med Rep. 2013 Nov;8(5):1432-8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2013.1692. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Mol Med Rep. 2013. PMID: 24065069
-
Targeting adenosine and regulatory T cells in cancer immunotherapy.Hum Immunol. 2021 Apr;82(4):270-278. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2020.12.005. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Hum Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33610376 Review.
-
Update on the Protective Role of Regulatory T Cells in Myocardial Infarction: A Promising Therapy to Repair the Heart.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2016 Dec;68(6):401-413. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000436. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27941502 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting regulatory T cells for cardiovascular diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 23;14:1126761. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1126761. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36911741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD73/adenosine axis exerts cardioprotection against hypobaric hypoxia-induced metabolic shift and myocarditis in a sex-dependent manner.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Mar 7;22(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01535-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38454449 Free PMC article.
-
Cu-DHM nanozymes treat flap ischemia-reperfusion injury by amplifying immune modulation in a cascade manner and inhibiting cell apoptosis.Bioact Mater. 2025 Jun 24;51:720-739. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.06.036. eCollection 2025 Sep. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 40641838 Free PMC article.
-
ACE Gene Mutations (rs577350502) in Early-Onset and Recurrent Myocardial Infarction: A Case Report and Review.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2024 Apr 20;17:163-169. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S455740. eCollection 2024. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38659693 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T cells: a promising new therapeutic target in ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 7;16:1514335. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1514335. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40260235 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

