A study of plithogenic graphs: applications in spreading coronavirus disease (COVID-19) globally
- PMID: 35401852
- PMCID: PMC8978528
- DOI: 10.1007/s12652-022-03772-6
A study of plithogenic graphs: applications in spreading coronavirus disease (COVID-19) globally
Erratum in
-
Correction to: A study of plithogenic graphs: applications in spreading coronavirus disease (COVID-19) globally.J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. 2022 Dec 6:1. doi: 10.1007/s12652-022-04483-8. Online ahead of print. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. 2022. PMID: 36530471 Free PMC article.
Abstract
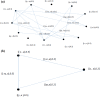
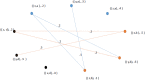
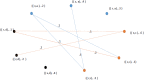
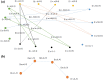
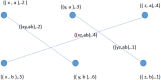
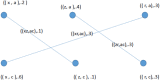
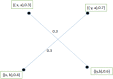
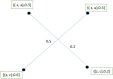
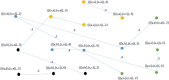
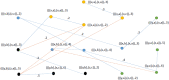
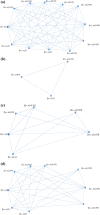
During the last two decades, the world has experienced three major outbreaks of Coronaviruses, namely severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS- CoV), middle east respiratory syndrome (MERS-CoV), and the current ongoing pandemic of severe acute respiratory syndrome 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The SARS-CoV-2 caused the disease known as Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Since its discovery for the first time in Wuhan, China, in December 2019, the disease has spread very fast, and cases have been reported in more than 200 countries/territories. In this study, the idea of Smarandache's pathogenic set is used to discuss the novel COVID-19 spread. We first introduced plithogenic graphs and their subclass, like plithogenic fuzzy graphs. We also established certain binary operations like union, join, Cartesian product, and composition of pathogenic fuzzy graphs, which are helpful when we discuss combining two different graphs. In the end, we investigate the spreading trend of COVID-19 by applying the pathogenic fuzzy graphs. We observe that COVID-19 is much dangerous than (MERS-CoV) and (SARS-CoV). Moreover, as the SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV outbreaks were controlled, there are greater chances to overcome the current pandemic of COVID-19 too. Our model suggests that all the countries should stop all types of traveling/movement across the borders and internally too to control the spread of COVID-19. The proposed model also predicts that in case precautionary measures have not been taken then there is a chance of severe outbreak in future.
Keywords: Graphs; Plithogenic graphs; Plithogenic sets.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAuthors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abdel-Basset M, Mohamed R. A novel plithogenic topsis-critic model for sustainable supply chain risk management. J Clean Prod. 2019;24:7119587. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119586. - DOI
-
- Abdel-Basset M, Mohamed R, Zaied ANH, Smarandache F. A hybrid plithogenic decision-making approach with quality function deployment for selecting supply chain sustainability metrics. Symmetry. 2019;11:903. doi: 10.3390/sym11070903. - DOI
-
- Akram M. Interval-valued fuzzy line graphs. Neural Comput Appl. 2012;21:145–150. doi: 10.1007/s00521-011-0733-0. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
