Para-Hydroxybenzyl Alcohol Delays the Progression of Neurodegenerative Diseases in Models of Caenorhabditis elegans through Activating Multiple Cellular Protective Pathways
- PMID: 35401930
- PMCID: PMC8989581
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8986287
Para-Hydroxybenzyl Alcohol Delays the Progression of Neurodegenerative Diseases in Models of Caenorhabditis elegans through Activating Multiple Cellular Protective Pathways
Abstract
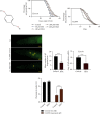
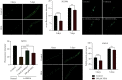
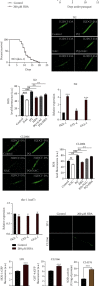
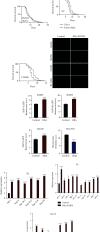
The traditional Chinese medicine Gastrodia elata (commonly called "Tianma" in Chinese) has been widely used in the treatment of rheumatism, epilepsy, paralysis, headache, and dizziness. Phenolic compounds, such as gastrodin, para-hydroxybenzyl alcohol (HBA), p-hydroxybenzaldehyde, and vanillin are the main bioactive components isolated from Gastrodia elata. These compounds not only are structurally related but also share similar pharmacological activities, such as antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activities, and effects on the treatment of aging-related diseases. Here, we investigated the effect of para-hydroxybenzyl alcohol (HBA) on neurodegenerative diseases and aging in models of Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans). Our results showed that HBA effectively delayed the progression of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and Huntington's disease in models of C. elegans. In addition, HBA could increase the average lifespan of N2 worms by more than 25% and significantly improve the age-related physiological functions of worms. Moreover, HBA improved the survival rate of worms under stresses of oxidation, heat, and pathogenic bacteria. Further mechanistic investigation revealed that HBA could activate FOXO/DAF-16 and SKN-1 to regulate antioxidative and xenobiotic metabolism pathway. HBA could also activate HSF-1 to regulate proteostasis maintenance pathway, mitochondrial unfolded stress response, endoplasmic stress response and autophagy pathways. The above results suggest that HBA activated multiple cellular protective pathways to increase stress resistance and protect against aging and aging-related diseases. Overall, our study indicates that HBA is a potential candidate for future development of antiaging pharmaceutical application.
Copyright © 2022 Yu Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- National Pharmacopoeia Committee. Pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China . Beijing: Chemical Industry Press; 2015.
-
- Shizhen L. In: Compendium of Materia Medica: Bencao Gangmu . Luo X., editor. Beijing: Foreign Languages Press; 2003. ISBN 7119032607.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

