Traditional Chinese Medicine Ginseng Dingzhi Decoction Ameliorates Myocardial Fibrosis and High Glucose-Induced Cardiomyocyte Injury by Regulating Intestinal Flora and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
- PMID: 35401934
- PMCID: PMC8989614
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9205908
Traditional Chinese Medicine Ginseng Dingzhi Decoction Ameliorates Myocardial Fibrosis and High Glucose-Induced Cardiomyocyte Injury by Regulating Intestinal Flora and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Abstract
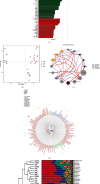
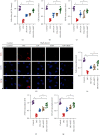
Myocardial fibrosis refers to the pathological changes of heart structure and morphology caused by various reasons of myocardial damage. It has become an important challenge in the later clinical treatment of acute myocardial infarction/ischemic cardiomyopathy or diabetes complicated with heart failure. Ginseng Dingzhi Decoction (GN), a Chinese herbal medicine, can reduce heart failure and protect cardiomyocytes. We infer that this may be related to the interaction with intestinal microbiota and mitochondrial homeostasis. The regulatory mechanism of GN on gut microbiota and mitochondria has not yet been elucidated. The intestinal microbiota was analyzed by the 16S rRNA gene; the fecal samples were sequenced and statistically analyzed to determine the changes of microbiota in the phenotype of heart failure rats. In addition, GN can regulate the microbial population that increases the proportion of short-chain fatty acids and anti-inflammatory bacteria and reduces the proportion of conditional pathogens to diabetic phenotype. The results suggest that GN may improve myocardial injury by regulating intestinal flora. Our data also show that stress-type heart failure caused by TAC (transverse aortic constriction) is accompanied by severe cardiac hypertrophy, reduced cardiac function, redox imbalance, and mitochondrial dysfunction. However, the use of GN intervention can significantly reduce heart failure and myocardial hypertrophy, improve heart function and improve myocardial damage, and maintain the mitochondrial homeostasis and redox of myocardial cells under high glucose stimulation. Interestingly, through in vitro experiments after TMBIM6 siRNA treatment, the improvement effect of GN on cell damage and the regulation of mitochondrial homeostasis were eliminated. TMBIM6 can indirectly regulate mitophagy and mitochondrial homeostasis to attenuate myocardial damage and confirms the regulatory effect of GN on mitophagy and mitochondrial homeostasis. We further intervened cardiomyocytes in high glucose through metformin (MET) and GN combination therapy. Research data show that MET and GN combination therapy can improve the level of mitophagy and protect cardiomyocytes. Our findings provide novel mechanistic insights for the treatment of diabetes combined with myocardial injury (myocardial fibrosis) and provide a pharmacological basis for the study of the combination of Chinese medicine and conventional diabetes treatment drugs.
Copyright © 2022 Junyan Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures









References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

