LncRNA B4GALT1-AS1 promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell growth via increasing ZEB1 level by sponging miR-144-3p
- PMID: 35402178
- PMCID: PMC8990218
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-22-296
LncRNA B4GALT1-AS1 promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell growth via increasing ZEB1 level by sponging miR-144-3p
Abstract
Background: Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are emerging as key players in the development and progression of cancer. Several malignancies involve dysregulated long noncoding ribonucleic acids (lncRNAs) in non-small cell lung cancer cell growth and their aggressive phenotypes. LncRNA B4GALT1-AS1 is important in the advancement of various malignancies, although its contribution to non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains unexplored.
Methods: LncRNA B4GALT1-AS1 in NSCLC tissues was detected and further validated in a cohort of non-small cell lung cancer tissues. The effects of lncRNA B4GALT1-AS1 on proliferation were determined by in vitro experiments. The B4GALT1-AS1-miR-144-3p-ZEB1 axis was assessed by dual-luciferase reporter and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays. Furthermore, the mechanism of B4GALT1-AS1 was investigated using loss-of-function assays in vitro.
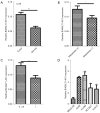
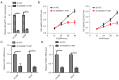
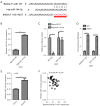
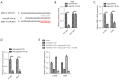
Results: We showed significant upregulation of B4GALT1-AS1 in cell lines and tissues of NSCLC. B4GALT1-AS1 knockdown impeded the in vitro proliferation-related characteristics of the NSCLC cells. The demonstration of the binding capacity of B4GALT1-AS1 and miR-144-3p was predicted by bioinformatics and luciferase reporter activity assay. The B4GALT1-AS1 and miR-144-3p interaction was shown by using rescue experiments. NSCLC has a positive association with its target, zinc finger e-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1).
Conclusions: In summary, the progression of NSCLC was facilitated by lncRNA B4GALT1-AS1 via interaction with miR-144-3p and positive regulation of ZEB1 expression.
Keywords: B4GALT1-AS1; Zinc finger e-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1); metastasis; miR-144-3p; non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
2022 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-22-296/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
