The efficacy and safety of dutasteride and finasteride in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35402192
- PMCID: PMC8984969
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-22-58
The efficacy and safety of dutasteride and finasteride in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Although the efficacy and safety of monotherapy in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) have been established clinically, the efficacy and safety of dutasteride and finasteride have not been compared. The aim was to systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of the two drugs in the treatment of BPH to provide medical evidence for clinical treatment.
Methods: A search of relevant articles was conducted using the electronic databases PubMed, Embase, Medline, Cochrane Library, China Academic Journals Full-text Database (CJFD), Chinese Science and Technology Journal Database (VIP) and Wanfang Database. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing the efficacy of finasteride (control group) with that of dutasteride (experimental group) in the treatment of BPH with respect to the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), the maximum urinary flow rate (Qmax), prostate volume (PV), quality of life (QOL), serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level and adverse drug reactions (ADRs) after medication were strictly evaluated and considered for inclusion. Rev Man 5.4 software was used for the meta-analysis.
Results: A total of 8 RCTs were included, with a total of 2,116, patients. The meta-analysis showed that compared with finasteride, dutasteride can effectively improve the Qmax of patients with BPH [mean difference (MD) =0.32; 95% confidence interval (CI): (0.01, 0.63); P=0.04]. There was no significant difference in reducing IPSS [MD =0.13; 95% CI: (-0.55, 0.82); P=0.70], improving PV [MD =-1.25; 95% CI: (-3.30, 0.79); P=0.23], reducing QOL [MD =-0.44; 95% CI: (-0.93, 0.05); P=0.08] and serum PSA level [MD =-0.04; 95% CI: (-0.15, 0.07); P=0.50], and the occurrence of ADRs [relative risk (RR) =-0.01; 95% CI: (-0.05, 0.04); P=0.72], there was no significant difference.
Discussion: Dutasteride is better than finasteride in improving the Qmax of patients with BPH. There was no statistically significant difference in symptoms, PV, PSA, QOL, or adverse reactions. Dutasteride is an effective and safe treatment for BPH. Due to the limitations of the methodological quality and sample size of the included studies, this conclusion needs to be verified by stratified RCTS with high volumes and long follow-up times.
Keywords: Dutasteride; benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH); finasteride; meta-analysis.
2022 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tau.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tau-22-58/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures






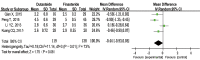
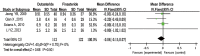


Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of dutasteride compared with finasteride in treating males with benign prostatic hyperplasia: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Aug;20(2):1566-1574. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8851. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32742388 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of baseline variables on changes in International Prostate Symptom Score after combined therapy with dutasteride plus tamsulosin or either monotherapy in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia and lower urinary tract symptoms: 4-year results of the CombAT study.BJU Int. 2014 Apr;113(4):623-35. doi: 10.1111/bju.12500. Epub 2014 Jan 9. BJU Int. 2014. PMID: 24127818 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparisons of the Efficacy and Safety of Finasteride and Dutasteride for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Network Meta-Analysis.Am J Ther. 2017 Sep/Oct;24(5):e517-e523. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000000326. Am J Ther. 2017. PMID: 26322675
-
Efficacy and Safety of Hexanic Lipidosterolic Extract of Serenoa repens (Permixon) in the Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Due to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Eur Urol Focus. 2016 Dec;2(5):553-561. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2016.04.002. Epub 2016 Apr 23. Eur Urol Focus. 2016. PMID: 28723522 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of Finasteride (5 alpha-reductase inhibitor) monotherapy in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia: A critical review of the literature.Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2020 Jan 13;91(4):205-210. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2019.4.205. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2020. PMID: 31937082 Review.
Cited by
-
Asparagi radix alleviates testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia by inhibiting 5α-reductase activity and androgen receptor signaling pathway.Nutr Res Pract. 2024 Dec;18(6):793-805. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2024.18.6.793. Epub 2024 Aug 19. Nutr Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 39651318 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting surgical efficacy and diagnosing histological inflammation: the clinical significance of prostate exosome proteins in benign prostatic hyperplasia.Transl Androl Urol. 2024 Jun 30;13(6):930-939. doi: 10.21037/tau-23-655. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Transl Androl Urol. 2024. PMID: 38983479 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Study of the Efficacy and Tolerability of Palmex® (Roystonea regia Lipid Extract), Saw Palmetto, Finasteride and Tamsulosin in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.Urol Res Pract. 2025 Mar 7;50(5):302-309. doi: 10.5152/tud.2025.24067. Urol Res Pract. 2025. PMID: 40248996 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Fenugreek Extract on Testosterone Propionate-Induced Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 31;26(3):1261. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031261. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39941027 Free PMC article.
-
Medical Advancements in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Treatments.Curr Urol Rep. 2024 May;25(5):93-98. doi: 10.1007/s11934-024-01199-4. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Curr Urol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38448685 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
