Effect of hypnosis before general anesthesia on postoperative outcomes in patients undergoing minor surgery for breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35402208
- PMCID: PMC8984985
- DOI: 10.21037/gs-22-114
Effect of hypnosis before general anesthesia on postoperative outcomes in patients undergoing minor surgery for breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Preoperative anxiety is a common phenomenon in breast cancer, causing pain and tension, which is not conducive to the effective surgical treatment and postoperative recovery. It is believed that hypnosis can change the patient's perception of pain, thereby improving the patient's ability to control pain. However, the results of studies for this topic were controversy. In order to explore the effect of hypnosis in breast cancer surgery we included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and conducted a meta analysis.
Methods: PubMed, Web of Science, Wiley online library, Elsevier, and Clinicaltrials.gov databases were searched by computer with the keywords "hypnosis/hypnotherapy" and "breast cancer" and "oncologic surgery/surgery/biopsy". After screening, the meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.4 software, and the evidence was rated using GRADE profiler 3.6 software.
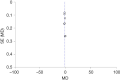
Results: A total of 1,242 patients were included in 8 studies, including 630 patients who received preoperative hypnosis and 612 patients who did not receive hypnosis. Meta-analysis showed that hypnosis before general anesthesia reduced the degree of preoperative anxiety (MD =-2.79, 95% CI: -3.93, -1.65, P<0.00001) and postoperative pain (MD =-1.25, 95% CI: -1.64, -0.86, P<0.00001) in patients undergoing breast cancer surgery, but had no effect on the operation time (MD =-6.30, 95% CI: -15.38, 2.78, P=0.17) and the incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting (OR =0.68, 95% CI: 0.22, 2.07, P=0.49).
Discussion: The application of hypnosis before general anesthesia for breast cancer surgery can reduce the degree of anxiety of patients, also reducing postoperative pain.
Keywords: Breast cancer; general anesthesia; hypnosis; meta-analysis.
2022 Gland Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://gs.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/gs-22-114/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Paravertebral anaesthesia with or without sedation versus general anaesthesia for women undergoing breast cancer surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 25;2(2):CD012968. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012968.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33629404 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a Hypnosis Session Before General Anesthesia on Postoperative Outcomes in Patients Who Underwent Minor Breast Cancer Surgery: The HYPNOSEIN Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Netw Open. 2018 Aug 3;1(4):e181164. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.1164. JAMA Netw Open. 2018. PMID: 30646110 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The advantages of hypnosis intervention on breast cancer surgery and adjuvant therapy.Breast. 2018 Feb;37:114-118. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2017.10.017. Epub 2017 Nov 11. Breast. 2018. PMID: 29136523
-
Postoperative analgesic effects of paravertebral block versus erector spinae plane block for thoracic and breast surgery: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 25;16(8):e0256611. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256611. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34432822 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of suggestive techniques in reducing postoperative side effects: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Anesth Analg. 2014 Dec;119(6):1407-19. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000466. Anesth Analg. 2014. PMID: 25289661 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Complementary Therapies on Patient-Reported Outcomes: An Overview of Recent Systematic Reviews in Oncology.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Sep 11;15(18):4513. doi: 10.3390/cancers15184513. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contemporary Nonpharmacological Strategies to Manage Preoperative Anxiety: Nonsystematic Review.Acta Med Litu. 2024;31(2):231-244. doi: 10.15388/Amed.2024.31.2.17. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Acta Med Litu. 2024. PMID: 40060256 Free PMC article.
-
Hypnosis support in anaesthesia is rarely used in German anaesthesia departments - a nationwide survey among leading physicians of anaesthesia departments.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Sep 6;24(1):314. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02705-4. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 39242504 Free PMC article.
-
Upskilling pain relief after surgery: a scoping review of perioperative behavioral intervention efficacy and practical considerations for implementation.Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2025 Feb 5;50(2):93-101. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2024-105601. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2025. PMID: 39909552 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting gene signature in breast cancer patients with multiple machine learning models.Discov Oncol. 2024 Oct 1;15(1):516. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01386-2. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39352418 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
