SARS-CoV-2 Diagnostics Based on Nucleic Acids Amplification: From Fundamental Concepts to Applications and Beyond
- PMID: 35402302
- PMCID: PMC8984495
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.799678
SARS-CoV-2 Diagnostics Based on Nucleic Acids Amplification: From Fundamental Concepts to Applications and Beyond
Abstract
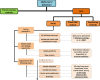
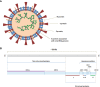
COVID-19 pandemic ignited the development of countless molecular methods for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 based either on nucleic acid, or protein analysis, with the first establishing as the most used for routine diagnosis. The methods trusted for day to day analysis of nucleic acids rely on amplification, in order to enable specific SARS-CoV-2 RNA detection. This review aims to compile the state-of-the-art in the field of nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) used for SARS-CoV-2 detection, either at the clinic level, or at the Point-Of-Care (POC), thus focusing on isothermal and non-isothermal amplification-based diagnostics, while looking carefully at the concerning virology aspects, steps and instruments a test can involve. Following a theme contextualization in introduction, topics about fundamental knowledge on underlying virology aspects, collection and processing of clinical samples pave the way for a detailed assessment of the amplification and detection technologies. In order to address such themes, nucleic acid amplification methods, the different types of molecular reactions used for DNA detection, as well as the instruments requested for executing such routes of analysis are discussed in the subsequent sections. The benchmark of paradigmatic commercial tests further contributes toward discussion, building on technical aspects addressed in the previous sections and other additional information supplied in that part. The last lines are reserved for looking ahead to the future of NAATs and its importance in tackling this pandemic and other identical upcoming challenges.
Keywords: NAATs; PCR; POCTs; SARS–CoV–2; diagnostics; isothermal amplification; molecular detection; viral sample processing.
Copyright © 2022 Vindeirinho, Pinho, Azevedo and Almeida.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alteri C., Cento V., Antonello M., Colagrossi L., Merli M., Ughi N., et al. (2020). Detection and Quantification of SARS-CoV-2 by Droplet Digital PCR in Real-Time PCR Negative Nasopharyngeal Swabs From Suspected COVID-19 Patients. PloS One 15 (9), e0236311–e0236311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236311 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

