Imaging and Risk Stratification in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Time to Include Right Ventricular Assessment
- PMID: 35402574
- PMCID: PMC8989834
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.797561
Imaging and Risk Stratification in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Time to Include Right Ventricular Assessment
Abstract
Background: Current European Society of Cardiology and European Respiratory Society guidelines recommend regular risk stratification with an aim of treating patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) to improve or maintain low-risk status (<5% 1-year mortality).
Methods: Consecutive patients with PAH who underwent cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (cMRI) were identified from the Assessing the Spectrum of Pulmonary hypertension Identified at a Referral centre (ASPIRE) registry. Kaplan-Meier survival curves, locally weighted scatterplot smoothing regression and multi-variable logistic regression analysis were performed.
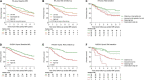
Results: In 311 consecutive, treatment-naïve patients with PAH undergoing cMRI including 121 undergoing follow-up cMRI, measures of right ventricular (RV) function including right ventricular ejection fraction (RVEF) and RV end systolic volume and right atrial (RA) area had prognostic value. However, only RV metrics were able to identify a low-risk status. Age (p < 0.01) and RVEF (p < 0.01) but not RA area were independent predictors of 1-year mortality.
Conclusion: This study highlights the need for guidelines to include measures of RV function rather than RA area alone to aid the risk stratification of patients with PAH.
Keywords: cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (cMRI); pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH); pulmonary hypertension; right atrial area; right ventricular (RV); risk stratification.
Copyright © 2022 Alandejani, Hameed, Tubman, Alabed, Shahin, Lewis, Dwivedi, Mahmood, Middleton, Watson, Alkhanfar, Johns, Rajaram, Garg, Condliffe, Elliot, Thompson, Rothman, Charalampopoulos, Lawrie, Wild, Swift and Kiely.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Galie N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the joint task force for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the European society of cardiology (ESC) and the European respiratory society (ERS): endorsed by: association for European paediatric and congenital cardiology (AEPC), international society for heart and lung transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Respir J. (2015) 46:903–75. 10.1183/13993003.01032-2015 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

