Nivolumab plus radiotherapy with or without temozolomide in newly diagnosed glioblastoma: Results from exploratory phase I cohorts of CheckMate 143
- PMID: 35402913
- PMCID: PMC8989388
- DOI: 10.1093/noajnl/vdac025
Nivolumab plus radiotherapy with or without temozolomide in newly diagnosed glioblastoma: Results from exploratory phase I cohorts of CheckMate 143
Abstract
Background: The phase 1 cohorts (1c+1d) of CheckMate 143 (NCT02017717) evaluated the safety/tolerability and efficacy of nivolumab plus radiotherapy (RT) ± temozolomide (TMZ) in newly diagnosed glioblastoma.
Methods: In total, 136 patients were enrolled. In part A (safety lead-in), 31 patients (n = 15, methylated/unknown MGMT promoter; n = 16, unmethylated MGMT promoter) received nivolumab and RT+TMZ (NIVO+RT+TMZ) and 30 patients with unmethylated MGMT promoter received NIVO+RT. In part B (expansion), patients with unmethylated MGMT promoter were randomized to NIVO+RT+TMZ (n = 29) or NIVO+RT (n = 30). Primary endpoint was safety/tolerability; secondary endpoint was overall survival (OS).
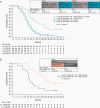
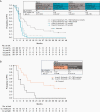
Results: NIVO+RT±TMZ was tolerable; grade 3/4 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 51.6% (NIVO+RT+TMZ) and 30.0% (NIVO+RT) of patients in part A and 46.4% (NIVO+RT+TMZ) and 28.6% (NIVO+RT) in part B. No new safety signals were detected. In part A, median OS (mOS) with NIVO+RT+TMZ was 33.38 months (95% CI, 16.2 to not estimable) in patients with methylated MGMT promoter. In patients with unmethylated MGMT promoter, mOS was 16.49 months (12.94-22.08) with NIVO+RT+TMZ and 14.41 months (12.55-17.31) with NIVO+RT. In part B, mOS was 14.75 months (10.01-18.6) with NIVO+RT+TMZ and 13.96 months (10.81-18.14) with NIVO+RT in patients with unmethylated MGMT promoter.
Conclusions: CheckMate 143 was the first trial evaluating immune checkpoint inhibition with first-line treatment of glioblastoma. Results showed that NIVO can be safely combined with RT±TMZ, with no new safety signals. Toxicities, including lymphopenia, were more frequent with NIVO+RT+TMZ. OS was similar with or without TMZ in patients with unmethylated MGMT promoter, and differences by MGMT methylation status were observed.
Keywords: PD-1; newly diagnosed glioblastoma; nivolumab; radiotherapy; temozolomide.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press, the Society for Neuro-Oncology and the European Association of Neuro-Oncology.
Figures

References
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(5):459–466. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):987–996. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
