High Expression of PEA15 Is Associated With Patient Survival in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
- PMID: 35403140
- PMCID: PMC8988953
- DOI: 10.21873/cdp.10049
High Expression of PEA15 Is Associated With Patient Survival in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
Abstract
Background/aim: Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is a rare but very aggressive tumor that is primarily pleural in origin. The 5-year overall survival rate of patients with MPM has not improved despite therapeutic advances. Therefore, biomarker discovery to identify premalignant or early malignant tumors of the mesothelium are crucial. PEA15 is a cytoplasmic protein that is involved in various human malignancies, including MPM. However, the clinicopathological involvement of PEA15 in MPM has not yet been documented.
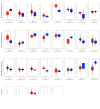
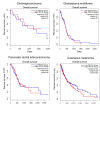
Materials and methods: The Oncomine database and GEPIA2 platform were used to analyze PEA15 mRNA expression and patient survival in patients with MPM.
Results: PEA15 was found to be significantly up-regulated in MPM, and this up-regulation inversely correlated with prolonged patient survival. Further, PEA15 expression was found to be increased in other cancer tissues without affecting overall survival.
Conclusion: PEA15 may represent a new potential prognostic biomarker in MPM patients.
Keywords: Mesothelioma; PEA15; bioinformatics; proteomics.
Copyright 2021, International Institute of Anticancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Lippolis R, De angelis M. Proteomics and human diseases. Journal of Proteomics & Bioinformatics. 2017;09(03):63–74. doi: 10.4172/jpb.1000391. - DOI
-
- Kuramitsu Y, Miyamoto H, Tanaka T, Zhang X, Fujimoto M, Ueda K, Tanaka T, Hamano K, Nakamura K. Proteomic differential display analysis identified upregulated astrocytic phosphoprotein PEA-15 in human malignant pleural mesothelioma cell lines. Proteomics. 2009;9(22):5078–5089. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200800284. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
