Global Transcriptomic Profiling Identifies Differential Gene Expression Signatures Between Inflammatory and Noninflammatory Aortic Aneurysms
- PMID: 35403833
- PMCID: PMC9902298
- DOI: 10.1002/art.42138
Global Transcriptomic Profiling Identifies Differential Gene Expression Signatures Between Inflammatory and Noninflammatory Aortic Aneurysms
Abstract
Objective: To identify hallmark genes and biomolecular processes in aortitis using high-throughput gene expression profiling, and to provide a range of potentially new drug targets (genes) and therapeutics from a pharmacogenomic network analysis.
Methods: Bulk RNA sequencing was performed on surgically resected ascending aortic tissues from inflammatory aneurysms (giant cell arteritis [GCA] with or without polymyalgia rheumatica, n = 8; clinically isolated aortitis [CIA], n = 17) and noninflammatory aneurysms (n = 25) undergoing surgical aortic repair. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the 2 patient groups were identified while controlling for clinical covariates. A protein-protein interaction model, drug-gene target information, and the DEGs were used to construct a pharmacogenomic network for identifying promising drug targets and potentially new treatment strategies in aortitis.
Results: Overall, tissue gene expression patterns were the most associated with disease state than with any other clinical characteristic. We identified 159 and 93 genes that were significantly up-regulated and down-regulated, respectively, in inflammatory aortic aneurysms compared to noninflammatory aortic aneurysms. We found that the up-regulated genes were enriched in immune-related functions, whereas the down-regulated genes were enriched in neuronal processes. Notably, gene expression profiles of inflammatory aortic aneurysms from patients with GCA were no different than those from patients with CIA. Finally, our pharmacogenomic network analysis identified genes that could potentially be targeted by immunosuppressive drugs currently approved for other inflammatory diseases.
Conclusion: We performed the first global transcriptomics analysis in inflammatory aortic aneurysms from surgically resected aortic tissues. We identified signature genes and biomolecular processes, while finding that CIA may be a limited presentation of GCA. Moreover, our computational network analysis revealed potential novel strategies for pharmacologic interventions and suggests future biomarker discovery directions for the precise diagnosis and treatment of aortitis.
© 2022 American College of Rheumatology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

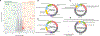



References
-
- Bossone E, Pluchinotta FR, Andreas M, Blanc P, Citro R, Limongelli G, et al. Aortitis. Vascul Pharmacol 2016;80:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Quimson L, Mayer A, Capponi S, Rea B, Rhee RL. Comparison of aortitis versus noninflammatory aortic aneurysms among patients who undergo open aortic aneurysm repair. Arthritis rheumatol 2020;72:1154–1159. - PubMed
-
- Ladich E, Yahagi K, Romero ME, Virmani R. Vascular diseases: aortitis, aortic aneurysms, and vascular calcification. Cardiovasc Pathol 2016;25:432–441. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

