Potent Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Efficacy of COVID-19 Hyperimmune Globulin from Vaccine-Immunized Plasma
- PMID: 35403837
- PMCID: PMC9108634
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202104333
Potent Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Efficacy of COVID-19 Hyperimmune Globulin from Vaccine-Immunized Plasma
Abstract
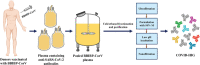
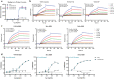
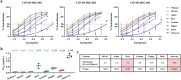
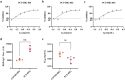
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) remains a global public health threat. Hence, more effective and specific antivirals are urgently needed. Here, COVID-19 hyperimmune globulin (COVID-HIG), a passive immunotherapy, is prepared from the plasma of healthy donors vaccinated with BBIBP-CorV (Sinopharm COVID-19 vaccine). COVID-HIG shows high-affinity binding to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike (S) protein, the receptor-binding domain (RBD), the N-terminal domain of the S protein, and the nucleocapsid protein; and blocks RBD binding to human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (hACE2). Pseudotyped and authentic virus-based assays show that COVID-HIG displays broad-spectrum neutralization effects on a wide variety of SARS-CoV-2 variants, including D614G, Alpha (B.1.1.7), Beta (B.1.351), Gamma (P.1), Kappa (B.1.617.1), Delta (B.1.617.2), and Omicron (B.1.1.529) in vitro. However, a significant reduction in the neutralization titer is detected against Beta, Delta, and Omicron variants. Additionally, assessments of the prophylactic and treatment efficacy of COVID-HIG in an Adv5-hACE2-transduced IFNAR-/- mouse model of SARS-CoV-2 infection show significantly reduced weight loss, lung viral loads, and lung pathological injury. Moreover, COVID-HIG exhibits neutralization potency similar to that of anti-SARS-CoV-2 hyperimmune globulin from pooled convalescent plasma. Overall, the results demonstrate the potential of COVID-HIG against SARS-CoV-2 infection and provide reference for subsequent clinical trials.
Keywords: COVID-19 hyperimmune globulin; SARS-CoV-2 variant; passive immunotherapy; sinopharm COVID-19 vaccine.
© 2022 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
X.M.Y., H.C.Y., and R.J. are employees of China National Biotec Group Company Limited; D.Y., H.L., J.Z.W., and Y.L.D. are employees of Chengdu Rongsheng Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd; D.Y., H.L., T.J.L., Y.Z., C.Y.L., D.M.D., D.X.F., D.B.Z., Y.L.H., T.D., Y.X., and R.Z. are employees of Beijing Tiantan Biological Products Co., Ltd; C.S.L., Y.H., Y.P., R.H., Y.T.X., L.F., X.L.L., Z.J.Z., D.M. J., F.F.W., J.H.Y., K.P., D.M.X., and Y.L.H. are employees of Sinopharm Wuhan Plasma‐derived Biotherapies Co., Ltd. Sinopharm Wuhan Plasma‐derived Biotherapies Co. Ltd. filed patents on the production method of COVID‐HIG to China National Intellectual Property Administration. All other authors declare no conflict of interest. Figure 6b,c has been amended on May 16, 2022, after initial online publication.
Figures



References
-
- Korber B., Fischer W. M., Gnanakaran S., Yoon H., Theiler J., Abfalterer W., Hengartner N., Giorgi E. E., Bhattacharya T., Foley B., Hastie K. M., Parker M. D., Partridge D. G., Evans C. M., Freeman T. M., de Silva T. I., Angyal A., Brown R. L., Carrilero L., Green L. R., Groves D. C., Johnson K. J., Keeley A. J., Lindsey B. B., Parsons P. J., Raza M., Rowland‐Jones S., Smith N., Tucker R. M., Wang D., et al., Cell 2020, 182, 812. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davies N. G., Abbott S., Barnard R. C., Jarvis C. I., Kucharski A. J., Munday J. D., Pearson C. A. B., Russell T. W., Tully D. C., Washburne A. D., Wenseleers T., Gimma A., Waites W., Wong K. L. M., van Zandvoort K., Silverman J. D., Diaz‐Ordaz K., Keogh R., Eggo R. M., Funk S., Jit M., Atkins K. E., Edmunds W. J., Science 2021, 372, eabg3055. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tegally H., Wilkinson E., Giovanetti M., Iranzadeh A., Fonseca V., Giandhari J., Doolabh D., Pillay S., San E. J., Msomi N., Mlisana K., von Gottberg A., Walaza S., Allam M., Ismail A., Mohale T., Glass A. J., Engelbrecht S., Van Zyl G., Preiser W., Petruccione F., Sigal A., Hardie D., Marais G., Hsiao N. Y., Korsman S., Davies M. A., Tyers L., Mudau I., York D., et al., Nature 2021, 592, 438. - PubMed
-
- Francisco R. d. S. Jr., Benites L. F., Lamarca A. P., de Almeida L. G. P., Hansen A. W., Gularte J. S., Demoliner M., Gerber A. L., de C Guimarães A. P., Antunes A. K. E., Heldt F. H., Mallmann L., Hermann B., Ziulkoski A. L., Goes V., Schallenberger K., Fillipi M., Pereira F., Weber M. N., de Almeida P. R., Fleck J. D., Vasconcelos A. T. R., Spilki F. R., Virus Res. 2021, 296, 198345. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
