Evaluation of Host Depletion and Extraction Methods for Shotgun Metagenomic Analysis of Bovine Vaginal Samples
- PMID: 35404108
- PMCID: PMC9045270
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.00412-21
Evaluation of Host Depletion and Extraction Methods for Shotgun Metagenomic Analysis of Bovine Vaginal Samples
Abstract
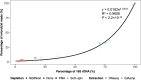
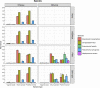
The reproductive tract metagenome plays a significant role in the various reproductive system functions, including reproductive cycles, health, and fertility. One of the major challenges in bovine vaginal metagenome studies is host DNA contamination, which limits the sequencing capacity for metagenomic content and reduces the accuracy of untargeted shotgun metagenomic profiling. This is the first study comparing the effectiveness of different host depletion and DNA extraction methods for bovine vaginal metagenomic samples. The host depletion methods evaluated were slow centrifugation (Soft-spin), NEBNext Microbiome DNA Enrichment kit (NEBNext), and propidium monoazide (PMA) treatment, while the extraction methods were DNeasy Blood and Tissue extraction (DNeasy) and QIAamp DNA Microbiome extraction (QIAamp). Soft-spin and QIAamp were the most effective host depletion method and extraction methods, respectively, in reducing the number of cattle genomic content in bovine vaginal samples. The reduced host-to-microbe ratio in the extracted DNA increased the sequencing depth for microbial reads in untargeted shotgun sequencing. Bovine vaginal samples extracted with QIAamp presented taxonomical profiles which closely resembled the mock microbial composition, especially for the recovery of Gram-positive bacteria. Additionally, samples extracted with QIAamp presented extensive functional profiles with deep coverage. Overall, a combination of Soft-spin and QIAamp provided the most robust representation of the vaginal microbial community in cattle while minimizing host DNA contamination. IMPORTANCE In addition to the host tissue collected during the sampling process, bovine vaginal samples are saturated with large amounts of extracellular DNA and secreted proteins that are essential for physiological purposes, including the reproductive cycle and immune defense. Due to the high host-to-microbe genome ratio, which hampers the sequencing efficacy for metagenome samples and the recovery of the actual metagenomic profiles, bovine vaginal samples cannot benefit from the full potential of shotgun sequencing. This is the first investigation on the most effective host depletion and extraction methods for bovine vaginal metagenomic samples. This study demonstrated an effective combination of host depletion and extraction methods, which harvested higher percentages of 16S rRNA genes and microbial reads, which subsequently led to a taxonomical profile that resembled the actual community and a functional profile with deeper coverage. A representative metagenomic profile is essential for investigating the role of the bovine vaginal metagenome for both reproductive function and susceptibility to infections.
Keywords: cattle; metagenomics; microbiome; shotgun; vagina; veterinary microbiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Host DNA depletion efficiency of microbiome DNA enrichment methods in infected tissue samples.J Microbiol Methods. 2020 Mar;170:105856. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2020.105856. Epub 2020 Jan 30. J Microbiol Methods. 2020. PMID: 32007505
-
Technical note: overcoming host contamination in bovine vaginal metagenomic samples with nanopore adaptive sequencing.J Anim Sci. 2022 Jan 1;100(1):skab344. doi: 10.1093/jas/skab344. J Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 34791313 Free PMC article.
-
Host DNA depletion methods and genome-centric metagenomics of bovine hindmilk microbiome.mSphere. 2024 Jan 30;9(1):e0047023. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00470-23. Epub 2023 Dec 6. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 38054728 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomic Sequencing for Microbial DNA in Human Samples: Emerging Technological Advances.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 16;23(4):2181. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042181. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metagenomics next-generation sequencing tests take the stage in the diagnosis of lower respiratory tract infections.J Adv Res. 2021 Sep 29;38:201-212. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.09.012. eCollection 2022 May. J Adv Res. 2021. PMID: 35572406 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification-Based Workflow for the Detection and Serotyping of Salmonella spp. in Environmental Poultry Flock Samples.Foods. 2024 Dec 17;13(24):4069. doi: 10.3390/foods13244069. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39767011 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating urine volume and host depletion methods to enable genome-resolved metagenomics of the urobiome.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 5:rs.3.rs-4688526. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4688526/v1. Res Sq. 2024. PMID: 39149494 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Short communication: imputation accuracy of host genomic data from metagenomic sequence information.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf175. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf175. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40380820
-
Choice of DNA extraction method affects detection of bacterial taxa from retail chicken breast.BMC Microbiol. 2022 Sep 30;22(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s12866-022-02650-7. BMC Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36180850 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Clinical Utility: Utilization of International Standards and Guidelines for Metagenomic Sequencing in Infectious Disease Diagnosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 15;25(6):3333. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063333. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542307 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hilton SK, Castro-Nallar E, Pérez-Losada M, Toma I, McCaffrey TA, Hoffman EP, Siegel MO, Simon GL, Johnson WE, Crandall KA. 2016. Metataxonomic and metagenomic approaches vs. culture-based techniques for clinical pathology. Front Microbiol 7:484–484. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2016.00484. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

