Patients with treated autoimmune hepatitis and persistent suppression of plasmacytoid dendritic cells: A different point of view
- PMID: 35404689
- PMCID: PMC9006358
- DOI: 10.1177/20587384211068667
Patients with treated autoimmune hepatitis and persistent suppression of plasmacytoid dendritic cells: A different point of view
Abstract
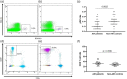
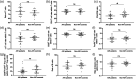
Objectives: Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) have been shown to have a role in autoimmune diseases, but their role in Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH) is not completely clear. In the present study, we assessed the frequency of pDCs in peripheral blood of AIH patients under long-term standard immunosuppressive therapy. Methods: This cross-sectional analysis enrolled 27 AIH patients and 27 healthy controls. We analyzed and compared their proportion of pDCs, CD4+, CD8+, γδ T cells, CD25+ regulatory T (Treg) cells, FoxP3+, Foxp3+CD39+ Treg cells, total B (CD19+) cells, and plasma cells (CD38+) in peripheral blood using flow cytometry immunophenotyping. Results: AIH patients had a lower percentage of pDCs (median frequencies of 0.2% vs. 0.4%; p = .002) and higher expression of CD8 T cells (32.5% vs 28.6%; p = 0.008) in peripheral blood, when compared to healthy controls. We did not find statistically significant differences between the groups regarding the other cell subtypes.Conclusion: Our data suggest a persistent suppression of pDCs in AIH patients, along with increased CD8 T cell activity, years after AIH diagnosis and despite of good clinical response to treatment, thus pointing to a role of pDCs in the AIH pathogenesis.
Keywords: autoimmune hepatitis; flow cytometry; plasmacytoid dendritic cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Wang J, Cao X, Zhao J, et al. (2017) Critical roles of conventional dendritic cells in promoting T cell-dependent hepatitis through regulating natural killer T cells: critical roles of conventional DC. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 188(1): 127–137. DOI: 10.1111/cei.12907. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

