Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: An Update on Their Use in the Separation of Active Compounds from Natural Products
- PMID: 35406265
- PMCID: PMC9003505
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14071389
Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: An Update on Their Use in the Separation of Active Compounds from Natural Products
Abstract
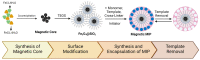
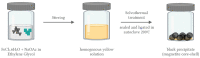
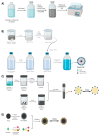
During the last few years, separation techniques using molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) have been developed, making breakthroughs using magnetic properties. Compared to conventional MIPs, magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers (MMIPs) have advantages in sample pretreatment due to their high specificity and selectivity towards analytes as a result of their larger specific surface areas and highly accessible specific binding sites. The techniques of isolation of active compounds from natural products usually require very long process times and low compound yields. When MMIPs are used in sample separation as Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) sorbents, the MMIPs are introduced into the dissolved sample and spread evenly, and they form bonds between the analyte and the MMIPs, which are then separated from the sample matrix using an external magnetic field. This process of separating analytes from the sample matrix makes the separation technique with MMIPs very simple and easy. This review discusses how to synthesize MMIPs, which factors must be considered in their synthesis, and their application in the separation of active compounds from natural products. MMIPs with magnetic core-shells made by co-precipitation can be a good choice for further development due to the high synthesis yield. Further optimization of the factors affecting the size and distribution of magnetic core-shell particles can obtain higher synthesis yields of MMIPs with higher adsorption capacity and selectivity. Thus, they can isolate target compounds from natural plants in high yields and purity.
Keywords: active compound separation; magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer; natural product.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Factors Affecting the Analytical Performance of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jul 25;14(15):3008. doi: 10.3390/polym14153008. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35893970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and application of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers in sample preparation.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018 Jul;410(17):3991-4014. doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-1013-y. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018. PMID: 29651522 Review.
-
Nano-sized magnetic core-shell and bulk molecularly imprinted polymers for selective extraction of amiodarone from human plasma.Anal Chim Acta. 2022 Mar 15;1198:339548. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2022.339548. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Anal Chim Acta. 2022. PMID: 35190133
-
Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for selective recognition of resveratrol in wine.J Chromatogr A. 2013 Jul 26;1300:112-8. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.02.018. Epub 2013 Feb 14. J Chromatogr A. 2013. PMID: 23481473
-
Magnetic MIPs: Synthesis and Applications.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2359:85-96. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1629-1_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34410661
Cited by
-
Factors Affecting the Analytical Performance of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jul 25;14(15):3008. doi: 10.3390/polym14153008. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35893970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogens and Progestogens in Environmental Waters: Analytical Chemistry and Biosensing Perspectives on Methods, Challenges, and Trends.Anal Chem. 2025 Apr 29;97(16):8654-8683. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c06796. Epub 2025 Apr 21. Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40254992 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Synergistic Removal of Diclofenac via Adsorption and Photocatalysis Using a Molecularly Imprinted Core-Shell Photocatalyst.Materials (Basel). 2025 May 15;18(10):2300. doi: 10.3390/ma18102300. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40429036 Free PMC article.
-
Molecularly Imprinted Microspheres in Active Compound Separation from Natural Product.Molecules. 2024 Aug 26;29(17):4043. doi: 10.3390/molecules29174043. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39274891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Fusion of Molecular Imprinting Technology and Siloxane Chemistry: A Way to Advanced Hybrid Nanomaterials.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Jan 6;13(2):248. doi: 10.3390/nano13020248. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36677999 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Atanasov A.G., Waltenberger B., Pferschy-Wenzig E.M., Linder T., Wawrosch C., Uhrin P., Temml V., Wang L., Schwaiger S., Heiss E.H., et al. Discovery and resupply of pharmacologically active plant-derived natural products: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015;33:1582–1614. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.08.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kumar S., Dhir A., Talwar S., Chakraborty D., Kaur P. What drives brand love for natural products? The moderating role of household size. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2021;58:102329. doi: 10.1016/j.jretconser.2020.102329. - DOI
-
- Allied Market Research Natural Food & Drinks Market. 2020. [(accessed on 20 January 2022)]. Available online: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/natural-food-and-drinks-market.
-
- Verma S., Singh S.P. Current and future status of herbal medicines. Vet. World. 2008;1:347–350. doi: 10.5455/vetworld.2008.347-350. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

