Chitosan as a Tool for Sustainable Development: A Mini Review
- PMID: 35406347
- PMCID: PMC9003291
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14071475
Chitosan as a Tool for Sustainable Development: A Mini Review
Abstract
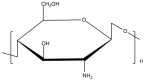
New developments require innovative ecofriendly materials defined by their biocompatibility, biodegradability, and versatility. For that reason, the scientific society is focused on biopolymers such as chitosan, which is the second most abundant in the world after cellulose. These new materials should show good properties in terms of sustainability, circularity, and energy consumption during industrial applications. The idea is to replace traditional raw materials with new ecofriendly materials which contribute to keeping a high production rate but also reducing its environmental impact and the costs. The chitosan shows interesting and unique properties, thus it can be used for different purposes which contributes to the design and development of sustainable novel materials. This helps in promoting sustainability through the use of chitosan and diverse materials based on it. For example, it is a good sustainable alternative for food packaging or it can be used for sustainable agriculture. The chitosan can also reduce the pollution of other industrial processes such as paper production. This mini review collects some of the most important advances for the sustainable use of chitosan for promoting circular economy. Hence, the present review focuses on different aspects of chitosan from its synthesis to multiple applications.
Keywords: biopolymers; chitosan; circular economy; sustainable development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Manigandan V., Karthik R., Ramachandran S., Rajagopal S. Chapter 15-Chitosan Applications in Food Industry. In: Grumezescu A.M., Holban A.M., editors. Biopolymers for Food Design. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2018. pp. 469–491.
-
- Pathania D., Gupta D., Kothiyal N.C., Sharma G., Eldesoky G.E., Naushad M. Preparation of a novel chitosan-g-poly(acrylamide)/Zn nanocomposite hydrogel and its applications for controlled drug delivery of ofloxacin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016;84:340–348. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.12.041. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources