YY1 Oligomerization Is Regulated by Its OPB Domain and Competes with Its Regulation of Oncoproteins
- PMID: 35406384
- PMCID: PMC8996997
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14071611
YY1 Oligomerization Is Regulated by Its OPB Domain and Competes with Its Regulation of Oncoproteins
Abstract
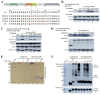
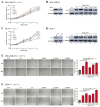
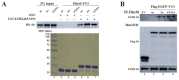
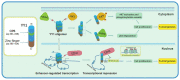
Yin Yang 1 (YY1) plays an oncogenic role through regulating the expression of various cancer-related genes and activating key oncoproteins. Previous research reported that YY1 protein formed dimers or oligomers without definite biological implications. In this study, we first demonstrated the oncoprotein binding (OPB) and zinc finger (ZF) domains of YY1 as the regions involved in its intermolecular interactions. ZFs are well-known for protein dimerization, so we focused on the OPB domain. After mutating three hydrophobic residues in the OPB to alanines, we discovered that YY1(F219A) and YY1(3A), three residues simultaneously replaced by alanines, were defective of intermolecular interaction. Meanwhile, the OPB peptide could robustly facilitate YY1 protein oligomerization. When expressed in breast cancer cells with concurrent endogenous YY1 knockdown, YY1(F219A) and (3A) mutants showed better capacity than wt in promoting cell proliferation and migration, while their interactions with EZH2, AKT and MDM2 showed differential alterations, especially with improved EZH2 binding affinity. Our study revealed a crucial role of the OPB domain in facilitating YY1 oligomerization and suggested a mutually exclusive regulation between YY1-mediated enhancer formation and its activities in promoting oncoproteins.
Keywords: OPB; YY1; oligomerization; oncoprotein; transcription factor; zinc finger.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures






References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

