Targeted Dual-Modal PET/SPECT-NIR Imaging: From Building Blocks and Construction Strategies to Applications
- PMID: 35406390
- PMCID: PMC8996983
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14071619
Targeted Dual-Modal PET/SPECT-NIR Imaging: From Building Blocks and Construction Strategies to Applications
Abstract
Molecular imaging is an emerging non-invasive method to qualitatively and quantitively visualize and characterize biological processes. Among the imaging modalities, PET/SPECT and near-infrared (NIR) imaging provide synergistic properties that result in deep tissue penetration and up to cell-level resolution. Dual-modal PET/SPECT-NIR agents are commonly combined with a targeting ligand (e.g., antibody or small molecule) to engage biomolecules overexpressed in cancer, thereby enabling selective multimodal visualization of primary and metastatic tumors. The use of such agents for (i) preoperative patient selection and surgical planning and (ii) intraoperative FGS could improve surgical workflow and patient outcomes. However, the development of targeted dual-modal agents is a chemical challenge and a topic of ongoing research. In this review, we define key design considerations of targeted dual-modal imaging from a topological perspective, list targeted dual-modal probes disclosed in the last decade, review recent progress in the field of NIR fluorescent probe development, and highlight future directions in this rapidly developing field.
Keywords: PET/SPECT imaging; dual-modal imaging; fluorescence-guided surgery; heptamethine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): a patent describing these probes has been submitted.
Figures

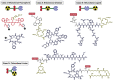

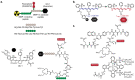
References
-
- van Dam G.M., Themelis G., Crane L.M., Harlaar N.J., Pleijhuis R.G., Kelder W., Sarantopoulos A., de Jong J.S., Arts H.J., van der Zee A.G., et al. Intraoperative tumor-specific fluorescence imaging in ovarian cancer by folate receptor-alpha targeting: First in-human results. Nat. Med. 2011;17:1315–1319. doi: 10.1038/nm.2472. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

