Functional and Phenotypic Characterization of Siglec-6 on Human Mast Cells
- PMID: 35406705
- PMCID: PMC8997871
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11071138
Functional and Phenotypic Characterization of Siglec-6 on Human Mast Cells
Abstract
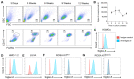
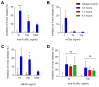
Mast cells are tissue-resident cells that contribute to allergic diseases, among others, due to excessive or inappropriate cellular activation and degranulation. Therapeutic approaches to modulate mast cell activation are urgently needed. Siglec-6 is an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM)-bearing receptor selectively expressed by mast cells, making it a promising target for therapeutic intervention. However, the effects of its engagement on mast cells are poorly defined. Siglec-6 expression and endocytosis on primary human mast cells and mast cell lines were assessed by flow cytometry. SIGLEC6 mRNA expression was examined by single-cell RNAseq in esophageal tissue biopsy samples. The ability of Siglec-6 engagement or co-engagement to prevent primary mast cell activation was determined based on assessments of mediator and cytokine secretion and degranulation markers. Siglec-6 was highly expressed by all mast cells examined, and the SIGLEC6 transcript was restricted to mast cells in esophageal biopsy samples. Siglec-6 endocytosis occurred with delayed kinetics relative to the related receptor Siglec-8. Co-crosslinking of Siglec-6 with FcεRIα enhanced the inhibition of mast cell activation and diminished downstream ERK1/2 and p38 phosphorylation. The selective, stable expression and potent inhibitory capacity of Siglec-6 on human mast cells are favorable for its use as a therapeutic target in mast cell-driven diseases.
Keywords: FcεRI; ITIM; Siglec-6; degranulation; endocytosis; mast cell; signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
W.K., A.X., T.L., J.S., J.L. and B.A.Y. are employees of and/or own stock and/or stock options from Allakos, Inc. M.E.R. is a consultant for Pulm One, Spoon Guru, ClostraBio, Serpin Pharm, Allakos, Celldex, Bristol Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, Ellodi Pharma, GlaxoSmithKline, Regeneron/Sanofi, Revolo Biotherapeutics, and Guidepoint and has an equity interest in the first six listed and royalties from reslizumab (Teva Pharmaceuticals), PEESSv2 (Mapi Research Trust), and UpToDate. M.E.R. is an inventor of patents owned by Cincinnati Children’s Hospital. J.B.W. is a consultant for Regeneron/Sanofi, Allakos, AstraZeneca, and Invea Therapeutics. B.S.B. received remuneration for serving on the scientific advisory board of Allakos, Inc. and owns stock in Allakos. He receives publication-related royalty payments from Elsevier and UpToDate®. He is a co-inventor on existing Siglec-8–related patents and thus may be entitled to a share of royalties received by Johns Hopkins University during development and potential sales of such products. B.S.B. is also a co-founder of Allakos, which makes him subject to certain restrictions under University policy. The terms of this arrangement are being managed by Johns Hopkins University and Northwestern University in accordance with their conflict of interest policies. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Kepley C.L., Taghavi S., Mackay G., Zhu D., Morel P.A., Zhang K., Ryan J.J., Satin L.S., Zhang M., Pandolfi P.P., et al. Co-aggregation of FcgammaRII with FcepsilonRI on human mast cells inhibits antigen-induced secretion and involves SHIP-Grb2-Dok complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:35139–35149. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404318200. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

