Understanding Molecular Mechanisms of Phenotype Switching and Crosstalk with TME to Reveal New Vulnerabilities of Melanoma
- PMID: 35406721
- PMCID: PMC8997563
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11071157
Understanding Molecular Mechanisms of Phenotype Switching and Crosstalk with TME to Reveal New Vulnerabilities of Melanoma
Abstract
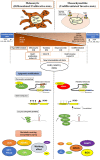
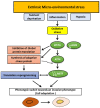
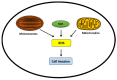
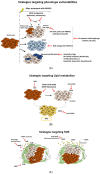
Melanoma cells are notorious for their high plasticity and ability to switch back and forth between various melanoma cell states, enabling the adaptation to sub-optimal conditions and therapeutics. This phenotypic plasticity, which has gained more attention in cancer research, is proposed as a new paradigm for melanoma progression. In this review, we provide a detailed and deep comprehensive recapitulation of the complex spectrum of phenotype switching in melanoma, the key regulator factors, the various and new melanoma states, and corresponding signatures. We also present an extensive description of the role of epigenetic modifications (chromatin remodeling, methylation, and activities of long non-coding RNAs/miRNAs) and metabolic rewiring in the dynamic switch. Furthermore, we elucidate the main role of the crosstalk between the tumor microenvironment (TME) and oxidative stress in the regulation of the phenotype switching. Finally, we discuss in detail several rational therapeutic approaches, such as exploiting phenotype-specific and metabolic vulnerabilities and targeting components and signals of the TME, to improve the response of melanoma patients to treatments.
Keywords: melanoma; metabolic reprogramming; oxidative stress; phenotype switching; therapeutic strategies; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Najem A., Krayem M., Perdrix A., Kerger J., Awada A., Journe F., Ghanem G. New Drug Combination Strategies in Melanoma: Current Status and Future Directions. Anticancer Res. 2017;37:5941–5953. - PubMed
-
- Shi H., Hugo W., Kong X., Hong A., Koya R.C., Moriceau G., Chodon T., Guo R., Johnson D.B., Dahlman K.B., et al. Acquired Resistance and Clonal Evolution in Melanoma during BRAF Inhibitor Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2014;4:80–93. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0642. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wouters J., Kalender-Atak Z., Minnoye L., Spanier K.I., De Waegeneer M., Bravo González-Blas C., Mauduit D., Davie K., Hulselmans G., Najem A., et al. Robust Gene Expression Programs Underlie Recurrent Cell States and Phenotype Switching in Melanoma. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020;22:986–998. doi: 10.1038/s41556-020-0547-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Verfaillie A., Imrichova H., Atak Z.K., Dewaele M., Rambow F., Hulselmans G., Christiaens V., Svetlichnyy D., Luciani F., Van den Mooter L., et al. Decoding the Regulatory Landscape of Melanoma Reveals TEADS as Regulators of the Invasive Cell State. Nat. Commun. 2015;6:6683. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7683. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

