Dietary Supplementation of Auricularia auricula-judae Polysaccharides Alleviate Nutritional Obesity in Mice via Regulating Inflammatory Response and Lipid Metabolism
- PMID: 35407029
- PMCID: PMC8997552
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11070942
Dietary Supplementation of Auricularia auricula-judae Polysaccharides Alleviate Nutritional Obesity in Mice via Regulating Inflammatory Response and Lipid Metabolism
Abstract
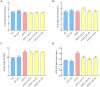
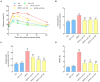
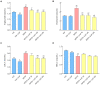
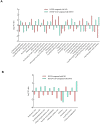
The incidence of lipid metabolism disorder and obesity that is caused by high-calorie diets is increasing year by year, which has become an urgent global health problem. This study was performed to explore the intervention effects of polysaccharides that were extracted from Auricularia auricula-judae resources in the Qinba Mountain area on nutritional obesity in C57BL/6J mice that was induced by high fat and high fructose diets (HFFD) and to investigate their underlying molecular mechanisms. The results showed that dietary supplementation of Auricularia auricula-judae polysaccharides (AAP) significantly improved mice's insulin resistance state, altered serum lipid metabolites, and slowed down body weight gain that was induced by HFFD. In addition, AAP supplementation decreased inflammatory factor levels and alleviated liver histomorphology changes. Furthermore, AAP down-regulated liver adipogenic-related gene expressions, suppressed cholesterol synthesis-related gene levels, up-regulated fatty acid β-oxidation-related gene expressions, and promoted cholesterol efflux-related gene expressions, thus improving mice hepatic lipid metabolism homeostasis. Moreover, the intervention effects were closely related to mitochondrial function. These results provide a scientific basis for the further development and utilization of Auricularia auricula-judae resources in the Qinba Mountain area.
Keywords: Auricularia auricula-judae polysaccharide; high-calorie diet; inflammatory response; lipid metabolism; nutritional obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ameliorating potential of Auricularia auricula-judae polysaccharides in mitigating hypercaloric diet-induced behavioral disorders through gut microbiota regulation.Front Nutr. 2025 May 29;12:1585778. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1585778. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40510494 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Auricularia auricula-judae (Bull.) Quél. polysaccharide acid hydrolysate on glucose metabolism in diabetic mice under oxidative stress.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jun;128:155485. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155485. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38640854
-
The In Vitro and In Vivo Antioxidant Capacities of Auricularia auricula-judae (Agaricomycetes) Polysaccharides Prepared via Free Radical-Mediated Methods.Int J Med Mushrooms. 2025;27(8):65-80. doi: 10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.2025058618. Int J Med Mushrooms. 2025. PMID: 40460404
-
The Current State and Future Prospects of Auricularia auricula's Polysaccharide Processing Technology Portfolio.Molecules. 2023 Jan 6;28(2):582. doi: 10.3390/molecules28020582. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36677640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review on Auricularia auricula-judae as a Functional Food: Growth, Chemical Composition, and Biological Activities.J Agric Food Chem. 2021 Feb 17;69(6):1739-1750. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c05934. Epub 2021 Feb 5. J Agric Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 33543932 Review.
Cited by
-
Auricularia auricula-judae Attenuates the Progression of Metabolic Syndrome in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Rats: Enzymatic Pre-Digestion Technology Is Superior to Superfine Grinding Method.Foods. 2024 Jan 26;13(3):406. doi: 10.3390/foods13030406. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38338541 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory and gut microbiota regulatory effects of ultrasonic degraded polysaccharides from Auricularia auricula-judae in DSS-induced colitis mice.Ultrason Sonochem. 2025 Jun;117:107339. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2025.107339. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Ultrason Sonochem. 2025. PMID: 40215791 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation, Purification, Fractionation, and Hepatoprotective Activity of Polygonatum Polysaccharides.Molecules. 2024 Feb 28;29(5):1038. doi: 10.3390/molecules29051038. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38474549 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Auricularia cornea var. Li. polysaccharides potential to improve hepatic, antioxidation and intestinal microecology in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Front Nutr. 2023 Jun 12;10:1161537. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1161537. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37377484 Free PMC article.
-
Structure Characterization, Antioxidant and Immunomodulatory Activities of Polysaccharide from Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn.Foods. 2022 Jun 22;11(13):1834. doi: 10.3390/foods11131834. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35804650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bluher M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019;15:288–298. - PubMed
-
- Van der Zande H.J.P., Lambooij J.M., Chavanelle V., Zawistowska-Deniziak A., Otero Y., Otto F., Lantier L., McGuinness O.P., Le Joubioux F., Giera M., et al. Effects of a novel polyphenol-rich plant extract on body composition, inflammation, insulin sensitivity, and glucose homeostasis in obese mice. Int. J. Obes. 2021;45:2016–2027. - PubMed
-
- Liu E., Ji Y., Zhang F., Liu B., Meng X. Review on Auricularia auricula-judae as a Functional Food: Growth, Chemical Composition, and Biological Activities. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2021;69:1739–1750. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

