Modified Breath Figure Methods for the Pore-Selective Functionalization of Honeycomb-Patterned Porous Polymer Films
- PMID: 35407174
- PMCID: PMC9000584
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12071055
Modified Breath Figure Methods for the Pore-Selective Functionalization of Honeycomb-Patterned Porous Polymer Films
Abstract
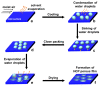
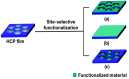
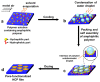
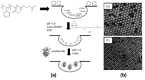
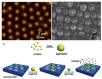
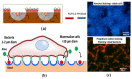
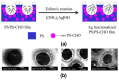
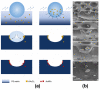
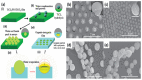
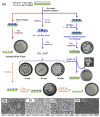
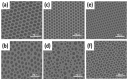
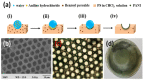
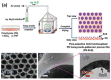
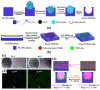
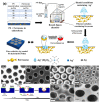
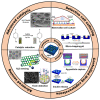
Recent developments in the field of the breath figure (BF) method have led to renewed interest from researchers in the pore-selective functionalization of honeycomb-patterned (HCP) films. The pore-selective functionalization of the HCP film gives unique properties to the film which can be used for specific applications such as protein recognition, catalysis, selective cell culturing, and drug delivery. There are several comprehensive reviews available for the pore-selective functionalization by the self-assembly process. However, considerable progress in preparation technologies and incorporation of new materials inside the pore surface for exact applications have emerged, thus warranting a review. In this review, we have focused on the pore-selective functionalization of the HCP films by the modified BF method, in which the self-assembly process is accompanied by an interfacial reaction. We review the importance of pore-selective functionalization, its applications, present limitations, and future perspectives.
Keywords: honeycomb-patterned porous film; interfacial reaction; modified breath figure method; pore-selective functionalization; self-assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





References
-
- Yabu H. Fabrication of honeycomb films by the breath figure technique and their applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2018;19:802–822. doi: 10.1080/14686996.2018.1528478. - DOI
-
- Yuan H., Li G., Dai E., Lu G., Huang X., Hao L., Tan Y. Ordered Honeycomb-Pattern Membrane. Chin. J. Chem. 2020;38:1767–1779. doi: 10.1002/cjoc.202000340. - DOI
-
- Mural P.K.S., Madras G., Bose S. Polymeric membranes derived from immiscible blends with hierarchical porous structures, tailored bio-interfaces and enhanced flux: Potential and key challenges. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects. 2018;14:149–165. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoso.2018.02.002. - DOI
-
- Vargas-Alfredo N., Santos-Coquillat A., Martínez-Campos E., Dorronsoro A., Cortajarena A.L., del Campo A., Rodríguez-Hernández J. Highly Efficient Antibacterial Surfaces Based on Bacterial/Cell Size Selective Microporous Supports. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2017;9:44270–44280. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b11337. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

