Measurement of the Photothermal Conversion Efficiency of CNT Films Utilizing a Raman Spectrum
- PMID: 35407219
- PMCID: PMC9000262
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12071101
Measurement of the Photothermal Conversion Efficiency of CNT Films Utilizing a Raman Spectrum
Abstract
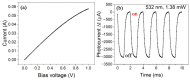
Because carbon nanotube (CNT) films have high photothermal conversion efficiency (PTCE), they have been widely used in bolometric and photothermoelectric photodetectors, seawater desalination, and cancer therapy. Here, we present a simple, quick, and non-destructive method to measure the PTCE of CNT films. According to the linear relationship between the Raman shift of the G+ peak and the temperature of a CNT, the offset of the G+ peak under varying excitation light power can characterize the changed temperature. Combining the simulation of the temperature distribution, the final value of the PTCE can be obtained. Finally, a CNT film with a high PTCE was chosen to be fabricated as a bolometric photodetector; a quite high responsivity (2 A W-1 at 532 nm) of this device demonstrated the effectiveness of our method.
Keywords: CNT film; Raman shift; photothermal conversion efficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

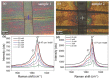
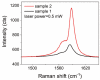
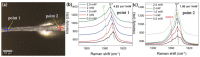
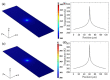
References
-
- Hu T., Chen K., Li L., Zhang J. Carbon nanotubes@silicone solar evaporators with controllable salt-tolerance for efficient water evaporation in a closed system. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2021;9:17502–17511. doi: 10.1039/D1TA03920B. - DOI
-
- Jian H., Qi Q., Wang W., Yu D. A Janus porous carbon nanotubes/poly (vinyl alcohol) composite evaporator for efficient solar-driven interfacial water evaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021;264:118459. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118459. - DOI
-
- Qin D.-D., Zhu Y.-J., Chen F.-F., Yang R.-L., Xiong Z.-C. Self-floating aerogel composed of carbon nanotubes and ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires for highly efficient solar energy-assisted water purification. Carbon. 2019;150:233–243. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.05.010. - DOI
-
- Zhang Q., Xu W., Wang X. Carbon nanocomposites with high photothermal conversion efficiency. Sci. China Mater. 2018;61:905–914. doi: 10.1007/s40843-018-9250-x. - DOI
-
- Zhao Y., Yuan H., Zhang X., Xue G., Tang J., Chen Y., Zhang X., Zhou W., Liu H. Laser-assisted synthesis of cobalt@N-doped carbon nanotubes decorated channels and pillars of wafer-sized silicon as highly efficient three-dimensional solar evaporator. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021;32:3090–3094. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2021.02.056. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

