Capturing Subtle Neurocognitive Differences in Children with and without Tourette Syndrome through a Fine-Grained Analysis of Design Fluency Profiles
- PMID: 35407554
- PMCID: PMC8999369
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11071946
Capturing Subtle Neurocognitive Differences in Children with and without Tourette Syndrome through a Fine-Grained Analysis of Design Fluency Profiles
Abstract
Background: Tourette syndrome (TS) can be accompanied by neurocognitive impairment. Only a few studies have focused on executive function assessment in TS using design fluency, providing preliminary results. This study aimed to characterize the detailed design fluency profile of children with TS compared with neurotypical children, while addressing the central concern of frequent comorbidities in studies on TS by considering tic severity and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms and diagnosis.
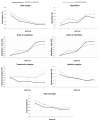
Methods: Sixty-one children aged between 6 and 15 years participated and were divided into a TS group (n = 28 (with ADHD n = 15)) and a control group (n = 33). Our objective was addressed by examining a wide range of measures of the Five-Point-Test, presumably sensitive to frontostriatal dysfunction. The total number of designs, repetitions, repetition ratio, unique designs, and numerical, spatial, and total strategies were examined for the total duration of the test (global measures) and at five equal time intervals (process measures).
Results: The TS group produced significantly fewer numerical strategies. Groups did not differ in other global or process measures. ADHD did not affect performance.
Conclusions: Children with TS do not inherently show general executive dysfunction but may present with subtle neurocognitive characteristics here revealed by comprehensive design fluency profiles.
Keywords: ADHD; Five-Point Test; Tourette syndrome; child; clinical neuropsychology; design fluency; executive function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®) American Psychiatric Pub.; Washington, DC, USA: 2013.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

