Feature Analysis and Extraction for Specific Emitter Identification Based on the Signal Generation Mechanisms of Radar Transmitters
- PMID: 35408230
- PMCID: PMC9003364
- DOI: 10.3390/s22072616
Feature Analysis and Extraction for Specific Emitter Identification Based on the Signal Generation Mechanisms of Radar Transmitters
Abstract
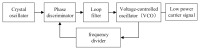
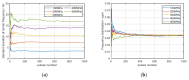
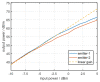
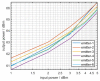
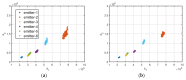
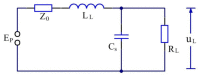
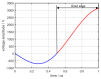
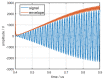
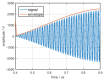
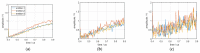
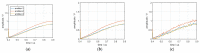
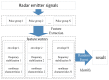
In this study, a feature analysis and extraction method was proposed for specific emitter identification based on the signal generation mechanisms of radar transmitters. The generation of radar signals by radar transmitters was analyzed theoretically and experimentally. In the analysis, the main source of unintentional modulation in radar signals was identified, and the frequency stabilization of the solid-state frequency source, the nonlinear characteristics of the radio frequency amplifier chain, and the envelope of the pulse front edge were extracted as features for specific emitter identification. Subsequently, these characteristics were verified through simulation. The results revealed that the features extracted by this method exhibit "fingerprint characteristics" and can be used to identify specific radar emitters.
Keywords: feature analysis and extraction; radar transmitter; signal generation mechanisms; specific emitter identification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Wang L. On Methods for Specific Radar Emitter Identification. Xidian University; Xi’an, China: 2016.
-
- Zhang G. Research on Emitter Identification. National University of Defense Technology; Changsha, China: 2005.
-
- Yang F. The Feature Extraction of Rader Source and Rader Individual Identification. Xidian University; Xi’an, China: 2017.
-
- Wan T., Fu X., Jiang K., Zhao Y., Tang B. Radar Antenna Scan Pattern Intelligent Recognition Using Visibility Graph. IEEE Access. 2019;7:175628–175641. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2957769. - DOI
-
- Guo Q., Yu X., Ruan G. LPI Radar Waveform Recognition Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Network Transfer Learning. Symmetry. 2019;11:540. doi: 10.3390/sym11040540. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

