Multi-Device Nutrition Control
- PMID: 35408231
- PMCID: PMC9003196
- DOI: 10.3390/s22072617
Multi-Device Nutrition Control
Abstract
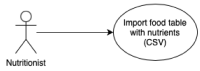
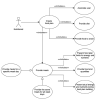
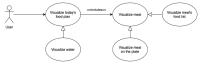
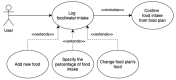
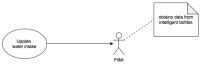
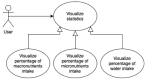
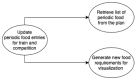
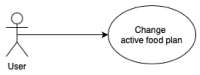
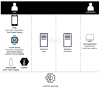
Precision nutrition is a popular eHealth topic among several groups, such as athletes, people with dementia, rare diseases, diabetes, and overweight. Its implementation demands tight nutrition control, starting with nutritionists who build up food plans for specific groups or individuals. Each person then follows the food plan by preparing meals and logging all food and water intake. However, the discipline demanded to follow food plans and log food intake results in high dropout rates. This article presents the concepts, requirements, and architecture of a solution that assists the nutritionist in building up and revising food plans and the user following them. It does so by minimizing human-computer interaction by integrating the nutritionist and user systems and introducing off-the-shelf IoT devices in the system, such as temperature sensors, smartwatches, smartphones, and smart bottles. An interaction time analysis using the keystroke-level model provides a baseline for comparison in future work addressing both the use of machine learning and IoT devices to reduce the interaction effort of users.
Keywords: IoT; food logging; food plans; machine learning; precision nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Afshin A., Sur P.J., Fay K.A., Cornaby L., Ferrara G., Salama J.S., Mullany E.C., Abate K.H., Abbafati C., Abebe Z., et al. Health effects of dietary risks in 195 countries, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2019;393:1958–1972. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30041-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wohlers E.M., Sirard J.R., Barden C.M., Moon J.K. Smart Phones are Useful for Food Intake and Physical Activity Surveys; Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society; Minneapolis, MN, USA. 3–6 September 2009; pp. 5183–5186. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tsai C.C., Lee G., Raab F., Norman G.J., Sohn T., Griswold W.G., Patrick K. Usability and Feasibility of PmEB: A Mobile Phone Application for Monitoring Real Time Caloric Balance. Mob. Networks Appl. 2007;12:173–184. doi: 10.1007/s11036-007-0014-4. - DOI
-
- Lo F.P.W., Sun Y., Qiu J., Lo B. A novel vision-based approach for dietary assessment using deep learning view synthesis; Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Conference on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN); Chicago, IL, USA. 19–22 May 2019; pp. 1–4.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

