Two High-Precision Proximity Capacitance CMOS Image Sensors with Large Format and High Resolution
- PMID: 35408384
- PMCID: PMC9002872
- DOI: 10.3390/s22072770
Two High-Precision Proximity Capacitance CMOS Image Sensors with Large Format and High Resolution
Abstract
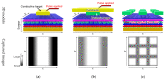
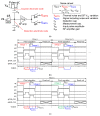
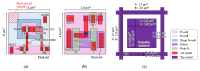
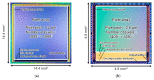
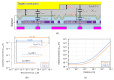
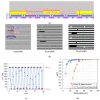
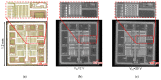
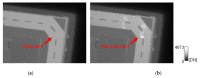
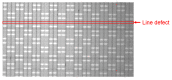
This paper presents newly developed two high-precision CMOS proximity capacitance image sensors: Chip A with 12 μm pitch pixels with a large detection area of 1.68 cm2; Chip B with 2.8 μm pitch 1.8 M pixels for a higher resolution. Both fabricated chips achieved a capacitance detection precision of less than 100 zF (10-19 F) at an input voltage of 20 V and less than 10 zF (10-20 F) at 300 V due to the noise cancelling technique. Furthermore, by using multiple input pulse amplitudes, a capacitance detection dynamic range of up to 123 dB was achieved. The spatial resolution improvement was confirmed by the experimentally obtained modulation transfer function for Chip B with various line and space pattens. The examples of capacitance imaging using the fabricated chips were also demonstrated.
Keywords: CMOS; high precision; high resolution; image sensor; large format; proximity capacitance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures









References
-
- Ohta J. Smart CMOS Image Sensors and Applications. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2020.
-
- Oike Y. Imaging Devices and Systems for Future Society; Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) Tutorial; Virtual. 12-16 December 2020.
-
- Viable Cell Density Sensors Process Analytics Hamilton Company. [(accessed on 7 February 2022)]. Available online: https://www.hamiltoncompany.com/process-analytics/sensors/cell-density-s....
-
- CCMT-10D CCMT-D Series Ceramic Capacitance Manometer Transducer Type Vacuum Gauge Products ULVAC SHOWCASE. [(accessed on 7 February 2022)]. Available online: https://showcase.ulvac.co.jp/en/products/vacuum-gauge/transducer-type-g-....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

