Neuroprotective Effects of Green Tea Seed Isolated Saponin Due to the Amelioration of Tauopathy and Alleviation of Neuroinflammation: A Therapeutic Approach to Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 35408478
- PMCID: PMC9000224
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27072079
Neuroprotective Effects of Green Tea Seed Isolated Saponin Due to the Amelioration of Tauopathy and Alleviation of Neuroinflammation: A Therapeutic Approach to Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
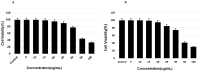
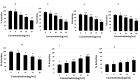
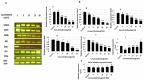
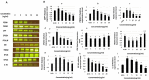
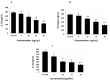
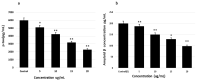
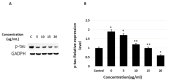
Tauopathy is one of the major causes of neurodegenerative disorders and diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD). Hyperphosphorylation of tau proteins by various kinases leads to the formation of PHF and NFT and eventually results in tauopathy and AD; similarly, neuroinflammation also exaggerates and accelerates neuropathy and neurodegeneration. Natural products with anti-tauopathy and anti-neuroinflammatory effects are highly recommended as safe and feasible ways of preventing and /or treating neurodegenerative diseases, including AD. In the present study, we isolated theasaponin E1 from ethanol extract of green tea seed and evaluated its therapeutic inhibitory effects on tau hyper-phosphorylation and neuroinflammation in neuroblastoma (SHY-5Y) and glioblastoma (HTB2) cells, respectively, to elucidate the mechanism of the inhibitory effects. The expression of tau-generating and phosphorylation-promoting genes under the effects of theasaponin E1 were determined and assessed by RT- PCR, ELISA, and western blotting. It was found that theasaponin E1 reduced hyperphosphorylation of tau and Aβ concentrations significantly, and dose-dependently, by suppressing the expression of GSK3 β, CDK5, CAMII, MAPK, EPOE4(E4), and PICALM, and enhanced the expression of PP1, PP2A, and TREM2. According to the ELISA and western blotting results, the levels of APP, Aβ, and p-tau were reduced by treatment with theasaponin E1. Moreover, theasaponin E1 reduced inflammation by suppressing the Nf-kB pathway and dose-dependently reducing the levels of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1beta, IL-6, and TNF-alpha etc.
Keywords: SHY-5Y cells; kinases; neurodegeneration; neurofibrillary tangles; neuroinflammation; taupathy.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors of this manuscript declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Green Tea Seed Isolated Theasaponin E1 Ameliorates AD Promoting Neurotoxic Pathogenesis by Attenuating Aβ Peptide Levels in SweAPP N2a Cells.Molecules. 2020 May 16;25(10):2334. doi: 10.3390/molecules25102334. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32429462 Free PMC article.
-
Rutin prevents tau pathology and neuroinflammation in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Jun 11;18(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02182-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34116706 Free PMC article.
-
Piper sarmentosum Roxb. confers neuroprotection on beta-amyloid (Aβ)-induced microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and attenuates tau hyperphosphorylation in SH-SY5Y cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 May 10;217:187-194. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.02.025. Epub 2018 Feb 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29462698
-
Therapeutic potentials of plant iridoids in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 1;169:185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30877973 Review.
-
Tauopathy in AD: Therapeutic Potential of MARK-4.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2024;21(11):779-790. doi: 10.2174/0115672050358397250126151707. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2024. PMID: 39931856 Review.
Cited by
-
Promising Natural Remedies for Alzheimer's Disease Therapy.Molecules. 2025 Feb 17;30(4):922. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040922. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alzheimer's Disease as a Major Public Health Concern: Role of Dietary Saponins in Mitigating Neurodegenerative Disorders and Their Underlying Mechanisms.Molecules. 2022 Oct 11;27(20):6804. doi: 10.3390/molecules27206804. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36296397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ameliorative role of Polyscias fruticosa leaf extract in aluminum chloride-induced neurotoxicity flies possibly mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonistic and anticholinesterase active compounds.J Nat Med. 2025 Jul 11. doi: 10.1007/s11418-025-01928-0. Online ahead of print. J Nat Med. 2025. PMID: 40646316
-
Therapeutic Candidates for Alzheimer's Disease: Saponins.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 22;24(13):10505. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310505. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes in neurodegenerative diseases: Therapeutic potential and modification methods.Neural Regen Res. 2026 Feb 1;21(2):478-490. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00720. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Neural Regen Res. 2026. PMID: 40326981 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

