Immune Checkpoint Receptors Signaling in T Cells
- PMID: 35408889
- PMCID: PMC8999077
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23073529
Immune Checkpoint Receptors Signaling in T Cells
Abstract
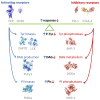
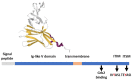
The characterization of the receptors negatively modulating lymphocyte function is rapidly advancing, driven by success in tumor immunotherapy. As a result, the number of immune checkpoint receptors characterized from a functional perspective and targeted by innovative drugs continues to expand. This review focuses on the less explored area of the signaling mechanisms of these receptors, of those expressed in T cells. Studies conducted mainly on PD-1, CTLA-4, and BTLA have evidenced that the extracellular parts of some of the receptors act as decoy receptors for activating ligands, but in all instances, the tyrosine phosphorylation of their cytoplasmatic tail drives a crucial inhibitory signal. This negative signal is mediated by a few key signal transducers, such as tyrosine phosphatase, inositol phosphatase, and diacylglycerol kinase, which allows them to counteract TCR-mediated activation. The characterization of these signaling pathways is of great interest in the development of therapies for counteracting tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte exhaustion/anergy independently from the receptors involved.
Keywords: DGK; ITIM; ITSM; PDL-1; SHIP; SHP-1; SHP-2; SLAM; Src.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


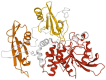

Similar articles
-
Effects of Src homology domain 2 (SH2)-containing inositol phosphatase (SHIP), SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase (SHP)-1, and SHP-2 SH2 decoy proteins on Fc gamma RIIB1-effector interactions and inhibitory functions.J Immunol. 2000 Jan 15;164(2):631-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.2.631. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10623804
-
Functional requirements for inhibitory signal transmission by the immunomodulatory receptor CD300a.BMC Immunol. 2012 Apr 26;13:23. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-13-23. BMC Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22537350 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis for positive and negative signaling by the natural killer cell receptor 2B4 (CD244).Blood. 2005 Jun 15;105(12):4722-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-09-3796. Epub 2005 Feb 15. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15713798
-
Inhibitory receptors, ITIM sequences and phosphatases.Curr Opin Immunol. 1997 Jun;9(3):338-43. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(97)80079-9. Curr Opin Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9203414 Review.
-
Negative regulation of immunoreceptor signaling.Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:669-707. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.20.081501.130710. Epub 2001 Oct 4. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11861615 Review.
Cited by
-
PD-1 immunology in the kidneys: a growing relationship.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 23;15:1458209. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1458209. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39507530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel strategy of co-expressing CXCR5 and IL-7 enhances CAR-T cell effectiveness in osteosarcoma.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 10;15:1462076. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1462076. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39450160 Free PMC article.
-
Lck Function and Modulation: Immune Cytotoxic Response and Tumor Treatment More Than a Simple Event.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 24;16(15):2630. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152630. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory immune checkpoints suppress the surveillance of senescent cells promoting their accumulation with aging and in age-related diseases.Biogerontology. 2024 Oct;25(5):749-773. doi: 10.1007/s10522-024-10114-w. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Biogerontology. 2024. PMID: 38954358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the putative role of PRDM1 and PRDM2 transcripts as mediators of T lymphocyte activation.J Transl Med. 2023 Mar 24;21(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04066-x. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36964555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baitsch L., Legat A., Barba L., Fuertes Marraco S.A., Rivals J.P., Baumgaertner P., Christiansen-Jucht C., Bouzourene H., Rimoldi D., Pircher H., et al. Extended co-expression of inhibitory receptors by human CD8 T-cells depending on differentiation, antigen-specificity and anatomical localization. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e30852. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030852. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sun L., Zhang L., Yu J., Zhang Y., Pang X., Ma C., Shen M., Ruan S., Wasan H.S., Qiu S. Clinical efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors for the treatment of advanced or metastatic cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:2083. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58674-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

