In Vitro and In Vivo Effects of the Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor WX-340 on Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines
- PMID: 35409084
- PMCID: PMC8999125
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23073724
In Vitro and In Vivo Effects of the Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor WX-340 on Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
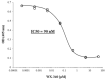
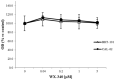
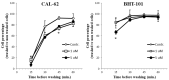
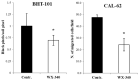
Increased expression of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) system is associated with tumor invasion, neo-angiogenesis, and metastatic spread, and has been shown to positively correlate with a poor prognosis in several cancer types, including thyroid carcinomas. In recent years, several uPA inhibitors were found to have anticancer effects in preclinical studies and in some phase II clinical trials, which prompted us to evaluate uPA as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of patients affected by the most aggressive form of thyroid cancer, the anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC). In this study, we evaluated the in vitro and in vivo effects of WX-340, a highly specific and selective uPA inhibitor, on two ATC-derived cell lines, CAL-62 and BHT-101. The results obtained indicated that WX-340 was able to reduce cell adhesion and invasiveness in a dose-dependent manner in both cell lines. In addition, WX-340 increased uPA receptor (uPAR) protein levels without affecting its plasma membrane concentration. However, this compound was unable to significantly reduce ATC growth in a xenograft model, indicating that uPA inhibition alone may not have the expected therapeutic effects.
Keywords: BHT-101; CAL-62; WX-340; anaplastic thyroid cancer; cell adhesion; cell migration; proliferation; urokinase plasminogen activator; xenograft.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential expression of a truncated form of the urokinase-type plasminogen-activator receptor in normal and tumor thyroid cells.Cancer Res. 1998 Mar 15;58(6):1315-9. Cancer Res. 1998. PMID: 9515821
-
High-affinity urokinase-derived cyclic peptides inhibiting urokinase/urokinase receptor-interaction: effects on tumor growth and spread.FEBS Lett. 2002 Sep 25;528(1-3):212-6. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03311-2. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 12297307
-
Inhibition of uPAR and uPA reduces invasion in papillary thyroid carcinoma cells.Laryngoscope. 2010 Jul;120(7):1383-90. doi: 10.1002/lary.20915. Laryngoscope. 2010. PMID: 20578104
-
Is there a role for urokinase-type plasminogen activator inhibitors as maintenance therapy in patients with ovarian cancer?Eur J Surg Oncol. 2017 Feb;43(2):252-257. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2016.06.002. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27345498 Review.
-
The urokinase plasminogen activator system: role in malignancy.Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10(1):39-49. doi: 10.2174/1381612043453559. Curr Pharm Des. 2004. PMID: 14754404 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular features of aggressive thyroid cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 20;12:1099280. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1099280. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36605433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma in the Kurdistan region of Iraq.BMC Surg. 2022 Oct 21;22(1):364. doi: 10.1186/s12893-022-01810-w. BMC Surg. 2022. PMID: 36271386 Free PMC article.
-
Is Melanoma Progression Affected by Thyroid Diseases?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 2;23(17):10036. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710036. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thyroid and renal cancers: A bidirectional association.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 23;12:951976. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.951976. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36212468 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: A Complex Condition Needing a Tailored Approach.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 7;12:954759. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.954759. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35875142 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howlader N., Noone A.M., Krapcho M., Miller D., Breast A., Yu M., Ruhl J., Tatalovich Z., Mariotto A., Lewis D.R., et al., editors. SEER Cancer Statistics Review. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD, USA: 2021. [(accessed on 25 February 2022)]. 1975–2012. Available online: http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2018/
-
- Trimboli P., Ulisse S., Graziano F.M., Marzullo A., Ruggieri M., Calvanese A., Piccirilli F., Cavaliere R., Fumarola A., D’Armiento M. Trend in thyroid carcinoma size, age at diagnosis, and histology in a retrospective study of 500 cases diagnosed over 20 years. Thyroid. 2006;16:1151–1155. doi: 10.1089/thy.2006.16.1151. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ulisse S., Bosco D., Nardi F., Nesca A., D’Armiento E., Guglielmino V., De Vito C., Sorrenti S., Pironi D., Tartaglia F., et al. Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System Score Combined with the New Italian Classification for Thyroid Cytology Improves the Clinical Management of Indeterminate Nodules. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2017;2017:9692304. doi: 10.1155/2017/9692304. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

