A Second Gamma-Glutamylpolyamine Synthetase, GlnA2, Is Involved in Polyamine Catabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor
- PMID: 35409114
- PMCID: PMC8998196
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23073752
A Second Gamma-Glutamylpolyamine Synthetase, GlnA2, Is Involved in Polyamine Catabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor
Abstract
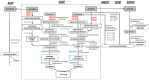
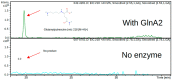
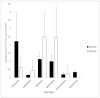
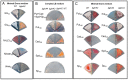
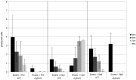
Streptomyces coelicolor is a soil bacterium living in a habitat with very changeable nutrient availability. This organism possesses a complex nitrogen metabolism and is able to utilize the polyamines putrescine, cadaverine, spermidine, and spermine and the monoamine ethanolamine. We demonstrated that GlnA2 (SCO2241) facilitates S. coelicolor to survive under high toxic polyamine concentrations. GlnA2 is a gamma-glutamylpolyamine synthetase, an enzyme catalyzing the first step in polyamine catabolism. The role of GlnA2 was confirmed in phenotypical studies with a glnA2 deletion mutant as well as in transcriptional and biochemical analyses. Among all GS-like enzymes in S. coelicolor, GlnA2 possesses the highest specificity towards short-chain polyamines (putrescine and cadaverine), while its functional homolog GlnA3 (SCO6962) prefers long-chain polyamines (spermidine and spermine) and GlnA4 (SCO1613) accepts only monoamines. The genome-wide RNAseq analysis in the presence of the polyamines putrescine, cadaverine, spermidine, or spermine revealed indication of the occurrence of different routes for polyamine catabolism in S. coelicolor involving GlnA2 and GlnA3. Furthermore, GlnA2 and GlnA3 are differently regulated. From our results, we can propose a complemented model of polyamine catabolism in S. coelicolor, which involves the gamma-glutamylation pathway as well as other alternative utilization pathways.
Keywords: GS-like enzymes; GlnA; GlnA2; GlnA3; Streptomyces coelicolor; nitrogen assimilation; polyamine catabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
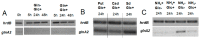

References
-
- Krysenko S., Okoniewski N., Kulik A., Matthews A., Grimpo J., Wohlleben W., Bera A. Gamma-Glutamylpolyamine Synthetase GlnA3 Is Involved in the First Step of Polyamine Degradation Pathway in Streptomyces coelicolor M145. Front. Microbiol. 2017;8:726. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00726. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Suzuki H., Kurihara S. Polyamine Catabolism in Prokaryotes. In: Kusano T., Suzuki H., editors. Polyamines: A Universal Molecular Nexus for Growth, Survival, and Specialized Metabolism. Springer; Tokyo, Japan: 2015. pp. 47–59.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

