The Activity of Ten Natural Extracts Combined in a Unique Blend to Maintain Cholesterol Homeostasis-In Vitro Model
- PMID: 35409162
- PMCID: PMC8998641
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23073805
The Activity of Ten Natural Extracts Combined in a Unique Blend to Maintain Cholesterol Homeostasis-In Vitro Model
Abstract
Background: Hypercholesterolemia is a major cause of cardiovascular disease and statins, the HMGCoA inhibitors, are the most prescribed drugs. Statins reduce the production of hepatic cholesterol, leading to greater expression of the LDL receptor and greater absorption of circulating LDL, reducing peripheral LDL levels. Unfortunately, statins are believed to induce myopathy and other severe diseases. To overcome this problem, safe nutraceuticals with the same activity as statins could hold great promise in the prevention and treatment of hypercholesterolemia. In this study, the anti-cholesterol efficacy of a new nutraceutical, called Esterol10®, was evaluated.
Methods: HepG2 cells were used to study the biological mechanisms exerted by Esterol10® analyzing different processes involved in cholesterol metabolism, also comparing data with Atorvastatin.
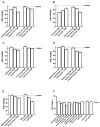
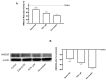
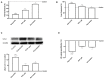
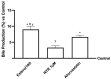
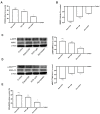
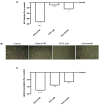
Results: Our results indicate that Esterol10® leads to a reduction in total hepatocyte cholesterol and an improvement in the biosynthesis of free cholesterol and bile acids. Furthermore, the anti-cholesterol activity of Esterol10® was also confirmed by the modulation of the LDL receptor and by the accumulation of lipids, as well as by the main intracellular pathways involved in the metabolism of cholesterol.
Conclusions: Esterol10® is safe and effective with anti-cholesterol activity, potentially providing an alternative therapy to those based on statins for hypercholesterolemia disease.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; cholesterol homeostasis; food supplement; low-density lipoprotein; monacolin K; nutraceuticals; statin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. F.U. and C.M. are co-founders of Noivita Srls.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Similarities and differences.Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997 May;32(5):403-25. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199732050-00005. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997. PMID: 9160173 Review.
-
New LDL-cholesterol lowering therapies: pharmacology, clinical trials, and relevance to acute coronary syndromes.Clin Ther. 2013 Aug;35(8):1082-98. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2013.06.019. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Clin Ther. 2013. PMID: 23932550 Review.
-
Keep recycling going: New approaches to reduce LDL-C.Biochem Pharmacol. 2019 Jun;164:336-341. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.04.003. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30953636 Review.
-
Consistency in efficacy and safety of ezetimibe coadministered with statins for treatment of hypercholesterolemia in women and men.J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2004 Dec;13(10):1101-7. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2004.13.1101. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2004. PMID: 15650343
-
Targeting PCSK9 as a promising new mechanism for lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Aug;164:183-94. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.04.011. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27133571 Review.
Cited by
-
Developing New Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges Complexes to Improve Vitamin D Absorption in an In Vitro Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 10;24(6):5322. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065322. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982396 Free PMC article.
-
An Innovative Probiotic-Based Supplement to Mitigate Molecular Factors Connected to Depression and Anxiety: An In Vitro Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 27;25(9):4774. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094774. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731995 Free PMC article.
-
The Combined Antioxidant Effects of N-Acetylcysteine, Vitamin D3, and Glutathione from the Intestinal-Neuronal In Vitro Model.Foods. 2024 Mar 1;13(5):774. doi: 10.3390/foods13050774. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38472887 Free PMC article.
-
The Combined Effect of Green Tea, Saffron, Resveratrol, and Citicoline against Neurodegeneration Induced by Oxidative Stress in an In Vitro Model of Cognitive Decline.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2024 Oct 1;2024:7465045. doi: 10.1155/2024/7465045. eCollection 2024. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2024. PMID: 39380915 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banach M., Bruckert E., Descamps O.S., Ellegård L., Ezhov M., Föger B., Fras Z., Kovanen P.T., Latkovskis G., März W., et al. The role of red yeast rice (RYR) supplementation in plasma cholesterol control: A review and expert opinion. Atheroscler. Suppl. 2019;39:e1–e8. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosissup.2019.08.023. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

