The Microbial Mechanisms of a Novel Photosensitive Material (Treated Rape Pollen) in Anti-Biofilm Process under Marine Environment
- PMID: 35409199
- PMCID: PMC8998240
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23073837
The Microbial Mechanisms of a Novel Photosensitive Material (Treated Rape Pollen) in Anti-Biofilm Process under Marine Environment
Abstract
Marine biofouling is a worldwide problem in coastal areas and affects the maritime industry primarily by attachment of fouling organisms to solid immersed surfaces. Biofilm formation by microbes is the main cause of biofouling. Currently, application of antibacterial materials is an important strategy for preventing bacterial colonization and biofilm formation. A natural three-dimensional carbon skeleton material, TRP (treated rape pollen), attracted our attention owing to its visible-light-driven photocatalytic disinfection property. Based on this, we hypothesized that TRP, which is eco-friendly, would show antifouling performance and could be used for marine antifouling. We then assessed its physiochemical characteristics, oxidant potential, and antifouling ability. The results showed that TRP had excellent photosensitivity and oxidant ability, as well as strong anti-bacterial colonization capability under light-driven conditions. Confocal laser scanning microscopy showed that TRP could disperse pre-established biofilms on stainless steel surfaces in natural seawater. The biodiversity and taxonomic composition of biofilms were significantly altered by TRP (p < 0.05). Moreover, metagenomics analysis showed that functional classes involved in the antioxidant system, environmental stress, glucose−lipid metabolism, and membrane-associated functions were changed after TRP exposure. Co-occurrence model analysis further revealed that TRP markedly increased the complexity of the biofilm microbial network under light irradiation. Taken together, these results demonstrate that TRP with light irradiation can inhibit bacterial colonization and prevent initial biofilm formation. Thus, TRP is a potential nature-based green material for marine antifouling.
Keywords: marine antifouling; microbial mechanisms; photosensitive material; rape pollen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



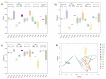



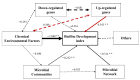


References
-
- Cui C.J., Chen A.R., Pan Z.C., Ma R.J. Two-dimensional numerical model and fast estimation method for calculating crevice corrosion of cross-sea bridges. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019;206:683–693. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.02.103. - DOI
-
- Qu G., Cai Y., Lv P., Ma X., Xie R., Xu Y., Ning P. Effect of EM microbial agent on aerobic composting for dairy cattle manure. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019;16:6945–6958. doi: 10.1007/s13762-018-2146-4. - DOI
-
- Xue J.H. Asymptotic analysis for buckling of undersea corroded pipelines. J. Press. Vessel Technol. 2008;130:021705. doi: 10.1115/1.2894293. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

