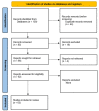
Neuroprotection in Stroke-Focus on the Renin-Angiotensin System: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 35409237
- PMCID: PMC8998496
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23073876
Neuroprotection in Stroke-Focus on the Renin-Angiotensin System: A Systematic Review
Abstract
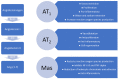
Stroke is the primary cause of disability in the adult population. Hypertension represents the leading risk factor being present in almost half the patients. The renin-angiotensin system is involved in the physiopathology of stroke and has an essential impact on hypertension as a risk factor. This article targeted the role of the renin-angiotensin system in stroke neuroprotection by reviewing the current literature available. The mechanism of action of the renin-angiotensin system was observed through the effects on AT1, AT2, and Mas receptors. The neuroprotective properties ascertained by angiotensin in stroke seem to be independent of the blood pressure reduction mechanism, and include neuroregeneration, angiogenesis, and increased neuronal resistance to hypoxia. The future relationship of stroke and the renin-angiotensin system is full of possibilities, as new agonist molecules emerge as potential candidates to restrict the impairment caused by stroke.
Keywords: neuroprotection; renin-angiotensin; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Virani S.S., Alonso A., Benjamin E.J., Bittencourt M.S., Callaway C.W., Carson A.P., Chamberlain A.M., Chang A.R., Cheng S., Delling F.N., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2020 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;141:e153–e639. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000757. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Feigin V.L., Roth G.A., Naghavi M., Parmar P., Krishnamurthi R., Chugh S., Mensah G.A., Norrving B., Shiue I., Ng M., et al. Global Burden of Stroke and Risk Factors in 188 Countries, during 1990–2013: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15:913–924. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30073-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials