Dexamethasone Attenuates the Expression of MMP-13 in Chondrocytes through MKP-1
- PMID: 35409238
- PMCID: PMC8998740
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23073880
Dexamethasone Attenuates the Expression of MMP-13 in Chondrocytes through MKP-1
Abstract
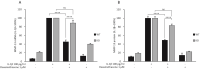
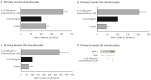
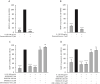
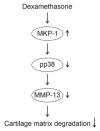
Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) is upregulated in inflammation and reduces the activity of proinflammatory mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAP kinases) by dephosphorylation. MAP kinases are intracellular signaling pathways that mediate the cellular effects of proinflammatory cytokines. In the present study, we investigated the effects of the glucocorticoid dexamethasone on the expression of catabolic enzymes in chondrocytes and tested the hypothesis that these effects are mediated through MKP-1. Dexamethasone was found to significantly attenuate the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-13 in human OA chondrocytes as well as in chondrocytes from MKP-1 WT mice, but not in chondrocytes from MKP-1 KO mice. Dexamethasone also increased the expression of MKP-1 in murine and human OA chondrocytes. Furthermore, p38 MAP kinase inhibitors significantly attenuated MMP-13 expression in human OA chondrocytes, while JNK MAP kinase inhibitors had no effect. The results indicate that the effect of dexamethasone on MMP-13 expression in chondrocytes was mediated by an MKP-1 and p38 MAP kinase-dependent manner. These findings, together with previous results, support the concept of MKP-1 as a protective factor in articular chondrocytes in inflammatory conditions and as a potential drug target to treat OA.
Keywords: MKP-1; MMP-13; chondrocyte; dexamethasone; inflammation; osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Downregulation of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1) expression in chondrocytes is regulated by MAP kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1).Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Jun;71:139-143. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.03.014. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30897501
-
Induction of matrix metalloproteinase-13 gene expression by TNF-alpha is mediated by MAP kinases, AP-1, and NF-kappaB transcription factors in articular chondrocytes.Exp Cell Res. 2003 Aug 1;288(1):208-17. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(03)00180-0. Exp Cell Res. 2003. PMID: 12878172
-
MyD88, IRAK1 and TRAF6 knockdown in human chondrocytes inhibits interleukin-1-induced matrix metalloproteinase-13 gene expression and promoter activity by impairing MAP kinase activation.Cell Signal. 2007 Dec;19(12):2549-57. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.08.013. Epub 2007 Aug 25. Cell Signal. 2007. PMID: 17905570
-
Aurothiomalate inhibits cyclooxygenase 2, matrix metalloproteinase 3, and interleukin-6 expression in chondrocytes by increasing MAPK phosphatase 1 expression and decreasing p38 phosphorylation: MAPK phosphatase 1 as a novel target for antirheumatic drugs.Arthritis Rheum. 2010 Jun;62(6):1650-9. doi: 10.1002/art.27409. Arthritis Rheum. 2010. PMID: 20178133
-
Dexamethasone suppresses monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 production via mitogen activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 dependent inhibition of Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in activated rat microglia.J Neurochem. 2007 Aug;102(3):667-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04535.x. Epub 2007 Apr 2. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17403137
Cited by
-
Dexamethasone: a double-edged sword in the treatment of osteoarthritis.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 7;15(1):11832. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96050-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40195473 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the interplay between autophagy and cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Dec 5;10:1089668. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1089668. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36544901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traumatic temporomandibular joint bony ankylosis in growing rats.BMC Oral Health. 2022 Dec 9;22(1):585. doi: 10.1186/s12903-022-02560-0. BMC Oral Health. 2022. PMID: 36494653 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT)-regulated, glucocorticoid receptor-dependent genes in macrophages reveals a novel host defense function of AAT.Physiol Rep. 2024 Jul;12(14):e16124. doi: 10.14814/phy2.16124. Physiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39016119 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

