The Roles of NEDD4 Subfamily of HECT E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Neurodevelopment and Neurodegeneration
- PMID: 35409239
- PMCID: PMC8999422
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23073882
The Roles of NEDD4 Subfamily of HECT E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Neurodevelopment and Neurodegeneration
Abstract
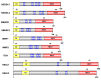
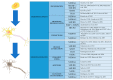
The ubiquitin pathway regulates the function of many proteins and controls cellular protein homeostasis. In recent years, it has attracted great interest in neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative diseases. Here, we have presented the first review on the roles of the 9 proteins of the HECT E3 ligase NEDD4 subfamily in the development and function of neurons in the central nervous system (CNS). We discussed their regulation and their direct or indirect involvement in neurodevelopmental diseases, such as intellectual disability, and neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease or Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Further studies on the roles of these proteins, their regulation and their targets in neurons will certainly contribute to a better understanding of neuronal function and dysfunction, and will also provide interesting information for the development of therapeutics targeting them.
Keywords: ALS; development; intellectual disability; ligases; neurodegenerative; ubiquitin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wang C., Dong K., Wang Y., Peng G., Song X., Yu Y., Shen P., Cui X. Integrating HECW1 expression into the clinical indicators exhibits high accuracy in assessing the prognosis of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2021;21:890. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08631-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

