Interdependence of Angiogenesis and Arteriogenesis in Development and Disease
- PMID: 35409246
- PMCID: PMC8999596
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23073879
Interdependence of Angiogenesis and Arteriogenesis in Development and Disease
Abstract
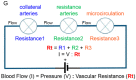
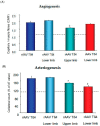
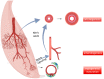
The structure of arterial networks is optimized to allow efficient flow delivery to metabolically active tissues. Optimization of flow delivery is a continuous process involving synchronization of the structure and function of the microcirculation with the upstream arterial network. Risk factors for ischemic cardiovascular diseases, such as diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia, adversely affect endothelial function, induce capillary regression, and disrupt the micro- to macrocirculation cross-talk. We provide evidence showing that this loss of synchronization reduces arterial collateral network recruitment upon arterial stenosis, and the long-term clinical outcome of current revascularization strategies in these patient cohorts. We describe mechanisms and signals contributing to synchronized growth of micro- and macrocirculation in development and upon ischemic challenges in the adult organism and identify potential therapeutic targets. We conclude that a long-term successful revascularization strategy should aim at both removing obstructions in the proximal part of the arterial tree and restoring "bottom-up" vascular communication.
Keywords: AAV; MRTF-A; Trio; angiogenesis; arteriogenesis; blood flow; endothelial cell shape; sFlt1; shear stress.
Conflict of interest statement
C.K. is holding IP on AAV-MRTF-A for therapeutic neovascularization. F.l.N. declares no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Klems A., van Rijssel J., Ramms A.S., Wild R., Hammer J., Merkel M., Derenbach L., Préau L., Hinkel R., Suarez-Martinez I., et al. The GEF Trio controls endothelial cell size and arterial remodeling downstream of Vegf signaling in both zebrafish and cell models. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:5319. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19008-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

