Viral Hepatitis, Cholesterol Metabolism, and Cholesterol-Lowering Natural Compounds
- PMID: 35409259
- PMCID: PMC8999150
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23073897
Viral Hepatitis, Cholesterol Metabolism, and Cholesterol-Lowering Natural Compounds
Abstract
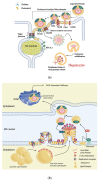
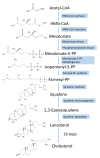
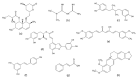
Hepatitis is defined as inflammation of the liver; it can be acute or chronic. In chronic cases, the prolonged inflammation gradually damages the liver, resulting in liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and sometimes liver failure or cancer. Hepatitis is often caused by viral infections. The most common causes of viral hepatitis are the five hepatitis viruses-hepatitis A virus (HAV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), hepatitis D virus (HDV), and hepatitis E virus (HEV). While HAV and HEV rarely (or do not) cause chronic hepatitis, a considerable proportion of acute hepatitis cases caused by HBV (sometimes co-infected with HDV) and HCV infections become chronic. Thus, many medical researchers have focused on the treatment of HBV and HCV. It has been documented that host lipid metabolism, particularly cholesterol metabolism, is required for the hepatitis viral infection and life cycle. Thus, manipulating host cholesterol metabolism-related genes and proteins is a strategy used in fighting the viral infections. Efforts have been made to evaluate the efficacy of cholesterol-lowering drugs, particularly 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors, in the treatment of hepatitis viral infections; promising results have been obtained. This review provides information on the relationships between hepatitis viruses and host cholesterol metabolism/homeostasis, as well as the discovery/development of cholesterol-lowering natural phytochemicals that could potentially be applied in the treatment of viral hepatitis.
Keywords: HMG-CoA reductase; cholesterol metabolism; hepatitis virus; phytochemicals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Stanaway J.D., Flaxman A.D., Naghavi M., Fitzmaurice C., Vos T., Abubakar I., Abu-Raddad L.J., Assadi R., Bhala N., Cowie B., et al. The global burden of viral hepatitis from 1990 to 2013: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2016;388:1081–1088. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30579-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Selitsky S.R., Dinh T.A., Toth C.L., Kurtz C.L., Honda M., Struck B.R., Kaneko S., Vickers K.C., Lemon S.M., Sethupathy P. Transcriptomic Analysis of Chronic Hepatitis B and C and Liver Cancer Reveals MicroRNA-Mediated Control of Cholesterol Synthesis Programs. mBio. 2015;6:e01500–e01515. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01500-15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

