More Prominent Inflammatory Response to Pachyman than to Whole-Glucan Particle and Oat-β-Glucans in Dextran Sulfate-Induced Mucositis Mice and Mouse Injection through Proinflammatory Macrophages
- PMID: 35409384
- PMCID: PMC8999416
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23074026
More Prominent Inflammatory Response to Pachyman than to Whole-Glucan Particle and Oat-β-Glucans in Dextran Sulfate-Induced Mucositis Mice and Mouse Injection through Proinflammatory Macrophages
Abstract
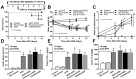
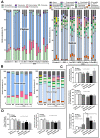
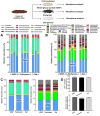
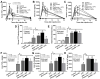
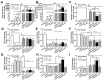
(1→3)-β-D-glucans (BG) (the glucose polymers) are recognized as pathogen motifs, and different forms of BGs are reported to have various effects. Here, different BGs, including Pachyman (BG with very few (1→6)-linkages), whole-glucan particles (BG with many (1→6)-glycosidic bonds), and Oat-BG (BG with (1→4)-linkages), were tested. In comparison with dextran sulfate solution (DSS) alone in mice, DSS with each of these BGs did not alter the weight loss, stool consistency, colon injury (histology and cytokines), endotoxemia, serum BG, and fecal microbiome but Pachyman-DSS-treated mice demonstrated the highest serum cytokine elicitation (TNF-α and IL-6). Likewise, a tail vein injection of Pachyman together with intraperitoneal lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced the highest levels of these cytokines at 3 h post-injection than LPS alone or LPS with other BGs. With bone marrow-derived macrophages, BG induced only TNF-α (most prominent with Pachyman), while LPS with BG additively increased several cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10); inflammatory genes (iNOS, IL-1β, Syk, and NF-κB); and cell energy alterations (extracellular flux analysis). In conclusion, Pachyman induced the highest LPS proinflammatory synergistic effect on macrophages, followed by WGP, possibly through Syk-associated interactions between the Dectin-1 and TLR-4 signal transduction pathways. Selection of the proper form of BGs for specific clinical conditions might be beneficial.
Keywords: DSS-induced mucositis; extracellular flux; mice; microbiome; proinflammatory macrophages; β-glucans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Chaiyasut C., Pengkumsri N., Sivamaruthi B., Sirilun S., Kesika P., Saelee M., Chaiyasut K., Peerajan S. Extraction of Β-glucan of Hericium erinaceus, Avena sativa, L., and Saccharomyces cerevisiae and in vivo evaluation of their immunomodulatory effects. Food Sci. Technol. 2018;38:138–146. doi: 10.1590/fst.18217. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

