Effective Remediation of Arsenic-Contaminated Soils by EK-PRB of Fe/Mn/C-LDH: Performance, Characteristics, and Mechanism
- PMID: 35410068
- PMCID: PMC8998996
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19074389
Effective Remediation of Arsenic-Contaminated Soils by EK-PRB of Fe/Mn/C-LDH: Performance, Characteristics, and Mechanism
Abstract
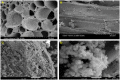
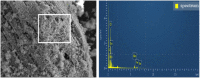
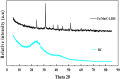
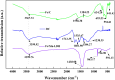
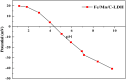
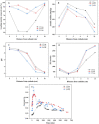
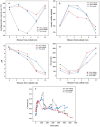
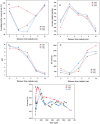
Arsenic is highly toxic and carcinogenic. The aim of the present work is to develop a good remediation technique for arsenic-contaminated soils. Here, a novel remediation technique by coupling electrokinetics (EK) with the permeable reactive barriers (PRB) of Fe/Mn/C-LDH composite was applied for the remediation of arsenic-contaminated soils. The influences of electric field strength, PRB position, moisture content and PRB filler type on the removal rate of arsenic from the contaminated soils were studied. The Fe/Mn/C-LDH filler synthesized by using bamboo as a template retained the porous characteristics of the original bamboo, and the mass percentage of Fe and Mn elements was 37.85%. The setting of PRB of Fe/Mn/C-LDH placed in the middle was a feasible option, with the maximum and average soil leaching toxicity removal rates of 95.71% and 88.03%, respectively. When the electric field strength was 2 V/cm, both the arsenic removal rate and economic aspects were optimal. The maximum and average soil leaching toxicity removal rates were similar to 98.40% and 84.49% of 3 V/cm, respectively. Besides, the soil moisture content had negligible effect on the removal of arsenic but slight effect on leaching toxicity. The best leaching toxicity removal rate was achieved when the soil moisture content was 35%, neither higher nor lower moisture content in the range of 25-45% was conducive to the improvement of leaching toxicity removal rate. The results showed that the EK-PRB technique could effectively remove arsenic from the contaminated soils. Characterizations of Fe/Mn/C-LDH indicated that the electrostatic adsorption, ion exchange, and surface functional group complexation were the primary ways to remove arsenic.
Keywords: arsenic-contaminated soil; electrokinetics; influence factor; permeable reactive barrier; remediation mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Pretreatment and Polarization Shielding on EK-PRB of Fe/Mn/C-LDH for Remediation of Arsenic Contaminated Soils.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Jan 12;13(2):325. doi: 10.3390/nano13020325. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36678078 Free PMC article.
-
Remediation of chromium-contaminated soil by electrokinetics and electrokinetics coupled with CaAl-LDH permeable reaction barrier.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Sep;24(25):20479-20486. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9705-y. Epub 2017 Jul 15. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28710730
-
Enhanced remediation of arsenic and chromium co-contaminated soil by eletrokinetic-permeable reactive barriers with different reagents.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Feb;26(4):3392-3403. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3842-9. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30511220
-
In situ stabilization of antimony and arsenic in co-contaminated soil using organic matter-Fe/Mn (hydr)oxides colloids and their mineral phase transformation.J Environ Sci (China). 2025 Oct;156:835-848. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2024.10.031. Epub 2024 Nov 9. J Environ Sci (China). 2025. PMID: 40412980 Review.
-
Electrokinetics applied in remediation of subsurface soil contaminated with chlorinated ethenes - A review.Chemosphere. 2019 Nov;235:113-125. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.075. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Chemosphere. 2019. PMID: 31255751 Review.
Cited by
-
Thermodynamics, Kinetics, and Mechanisms of the Co-Removal of Arsenate and Arsenite by Sepiolite-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron in Aqueous Solution.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 10;19(18):11401. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191811401. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36141677 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging the One Health concept for arsenic sustainability.Eco Environ Health. 2024 Mar 7;3(3):392-405. doi: 10.1016/j.eehl.2024.02.006. eCollection 2024 Sep. Eco Environ Health. 2024. PMID: 39281074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the Phytoremediation Potential of the Sinapis alba Plant Using Extractable Metal Concentrations.Plants (Basel). 2023 Aug 30;12(17):3123. doi: 10.3390/plants12173123. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37687367 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Pretreatment and Polarization Shielding on EK-PRB of Fe/Mn/C-LDH for Remediation of Arsenic Contaminated Soils.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Jan 12;13(2):325. doi: 10.3390/nano13020325. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36678078 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jeon E.K., Ryu S.R., Beak K. Application of solar-cells in the electrokinetic remediation of As-contaminated soil. Electrochim. Acta. 2015;181:160–166. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2015.03.065. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

