A case study: a continuous improvement project of lecturing skills for clinical teachers in Chinese residency standardized training
- PMID: 35410273
- PMCID: PMC8996608
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-022-03311-z
A case study: a continuous improvement project of lecturing skills for clinical teachers in Chinese residency standardized training
Abstract
Background: Aiming at the poor quality of small lectures due to the lack of lecturing skills of the clinical teachers in residency standardized training, the Teaching and Training Department of Shanghai East Hospital set up a continuous improvement project of lecturing skills for the clinical teachers to search for effective ways to improve lecture quality, then the effect was evaluated.
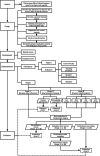
Methods: Based on the ADDIE model of training design, the department conducted the project in accordance with a process of analysis, design, development, implementation and evaluation. A special course "Clinical Teacher Presentation Training" (CTPT) was developed to convey and train the 5 key behaviors in presentation to improving lecture quality of the clinical teachers. Ninety-nine clinical teachers who give lectures to the residents were recruited as subjects for the project. Adopted the model of "intensive training + practice transference" to strengthen lecturing skills, and applied the Kirkpatrick Four Levels to evaluate the effect of the project from multi-role and multi-stage.
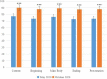
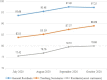
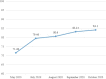
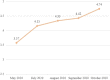
Results: The training satisfaction of the CTPT course from the subjects reaches 100%. The subjects have a high degree of knowledge acquisition through CTPT and the knowledge of the 5 key behaviors has been actually used in their lectures at the stage of practice transference. Comparing the data before training and after transference, it is found that the average increasing of the subjects' 5 key behavior scores made by teaching secretaries is 14.12 points (14.12%) and that of the subjects' self-efficacy scores is 9.31 points (9.31%); the performance values were modeling based on the scores from different types of evaluators and increased by an average of 12.61 points (12.61%); and the star ratings of the overall performance increased by an average of 1.17 points (23.4%). The results showed statistically difference (P < 0.001).
Conclusions: The project effectively promoted the improvement of the clinical teachers' lecturing skills and the quality of small lectures.
Keywords: ADDIE; Clinical teacher for the residency standardized training; Kirkpatrick’s evaluation; Lecturing skills improvement; Training transference.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evaluation of clinical teaching quality in competency-based residency training in Lithuania.Medicina (Kaunas). 2017 Dec;53(5):339-347. doi: 10.1016/j.medici.2017.08.002. Epub 2017 Sep 7. Medicina (Kaunas). 2017. PMID: 29074340
-
Application of flipped classroom teaching method based on ADDIE concept in clinical teaching for neurology residents.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Apr 3;24(1):366. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05343-z. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 38570778 Free PMC article.
-
Satisfaction of Clinical Teachers on Standardized Residency Training Program (SRTP) in China: A Cross-Sectional Survey.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 May 6;19(9):5676. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095676. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35565071 Free PMC article.
-
Application of practical training scenario simulation teaching method oriented to strengthen clinical skills in the clinical internship stage of medical students.Med Educ Online. 2025 Dec;30(1):2500557. doi: 10.1080/10872981.2025.2500557. Epub 2025 May 5. Med Educ Online. 2025. PMID: 40324061 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of Trauma Surgery Technical Skills Training Courses.J Surg Educ. 2019 May-Jun;76(3):832-843. doi: 10.1016/j.jsurg.2018.10.004. Epub 2019 Mar 1. J Surg Educ. 2019. PMID: 30827743
Cited by
-
Significance of Ongoing Training and Professional Development in Optimizing Healthcare-associated Infection Prevention and Control.J Med Signals Sens. 2024 Jul 2;14:13. doi: 10.4103/jmss.jmss_37_23. eCollection 2024. J Med Signals Sens. 2024. PMID: 39100741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of combined teaching method of case-based-learning and clinical pathway in practical gynecological teaching.PeerJ. 2024 Jul 24;12:e17813. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17813. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39071127 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Wang C, Qi X, Chen X, et al. The establishment of China standardized residency training system. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015;95(14):1041–1043. - PubMed
-
- Liu CX, Ouyang WW, Wang XW, et al. Comparing hybrid problem-based and lecture learning (PBL + LBL) with LBL pedagogy on clinical curriculum learning for medical students in China: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99(16):e19687. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019687. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

