Peripheral lymphocyte populations in ovarian cancer patients and correlations with clinicopathological features
- PMID: 35410290
- PMCID: PMC8996636
- DOI: 10.1186/s13048-022-00977-3
Peripheral lymphocyte populations in ovarian cancer patients and correlations with clinicopathological features
Abstract
Background: To investigate the alterations of peripheral lymphocyte subpopulations in ovarian cancer patients compared to benign or borderline counterparts. The possible clinicopathological implications were also evaluated.
Methods: We enrolled 112 treatment-naive ovarian cancer patients, 14 borderline tumor patients and 44 benign tumor patients between 09/2016 and 01/2019. Flow cytometry was used to measure the peripheral lymphocyte subsets consisting of T cells (CD3+, CD3+CD4+, CD3+CD8+ and CD8+CD28+), regulatory T cells (Tregs, CD4+CD25+CD127-), natural killer cells (NK cells, CD3-CD56+) and B cells (CD19+).
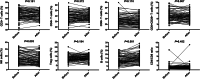
Results: Most ovarian cancer patients were high-grade serous carcinoma (84.8%), followed by clear cell carcinoma (8.03%). Late-stage tumor (FIGO III + IV) accounted for 82.1%. The study showed that the proportions of peripheral lymphocyte subsets underwent apparent changes in ovarian cancer patients. We observed elevated levels of Treg cells in patients with both ovarian borderline and malignant tumor compared to those with benign tumors, which achieved statistic significance. In contrast, CD3+CD8+ T and CD8+CD28+ T cells were significantly lower in ovarian cancer patients. Interestingly, low level of B cells was correlated to clear cell carcinoma (P = 0.024), advanced tumor (P = 0.028) and platinum-resistant recurrence (P = 0.014). Regarding the changes of lymphocyte subsets after surgery, CD8+CD28+ T cells had a significant decreasing tendency (P = 0.007) while B cells were the opposite (P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Ovarian cancer patients have altered circulating lymphocyte profile (elevated Treg cell, depressed CD3+CD8+ T and CD8+CD28+ T cells). Low level of B cells might be related to disease aggressiveness, and it recovered after the removal of tumor, which merits further study.
Keywords: Flow cytometry; Lymphocyte; Ovarian Neoplasms; Subpopulation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Sato E, Olson SH, Ahn J, Bundy B, Nishikawa H, Qian F, et al. Intraepithelial CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and a high CD8+/regulatory T cell ratio are associated with favorable prognosis in ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:18538–18543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509182102. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wouters MC, Komdeur FL, Workel HH, Klip HG, Plat A, Kooi NM, et al. Treatment regimen, surgical outcome, and t-cell differentiation influence prognostic benefit of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:714–724. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1617. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

