Retinoids as anti-cancer agents and their mechanisms of action
- PMID: 35411232
- PMCID: PMC8984900
Retinoids as anti-cancer agents and their mechanisms of action
Abstract
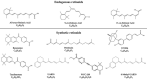
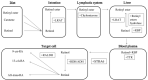
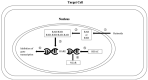
Retinoids (vitamin A) have been reported extensively for anti-cancer properties due to their high receptor-binding affinities and gene regulation abilities. However, the anti-cancer potential of retinoids has not been reviewed in recent years. Thus, this review focused on the anti-cancer effects of retinoids and their synergistic effects with other drugs, together with their mechanisms of action in different types of cancers reported in the past five years. The retinoids were well studied in breast cancer, melanoma, and colorectal cancer. Synthetic retinoids have shown higher selectivity, stronger effectiveness, and lower toxicity than endogenous retinoids. Interestingly, the combination treatment of endogenous retinoids with chemotherapy drugs showed enhanced anti-cancer effects. The mechanisms of action reported for retinoids mainly involved the RAR/RXR signaling pathway. However, limited clinical studies were conducted in recent years. Thus, retinoids which are highly potential anti-cancer agents are worth further study in clinical, especially as a combination therapy with chemotherapy drugs.
Keywords: All-trans-retinoic acid; RAR/RXR signaling pathway; combination treatment; vitamin A.
AJCR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Tang R, Liang C, Shangguan J, Guo S. The effects of all-trans retinoic acid on vasculogenic mimicry formation ability in CD133+ glioma stem cells and its mechanisms. J Biosci Med. 2017;5:42–54.
-
- Reddy RK, Comaratta M. Interlinks between vitamin A and retinopathy. Handb Nutr Food. 2019;2:397–414.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
